Extraintestinal Manifestations Of Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Clinical Aspects And Pathogenesis
Sandro da Costa Ferreira*, Bernardo Bezerra Martins de Oliveira, André Marussi Morsoletto, Ana de Lourdes Candolo Martinelli, Luiz Ernesto de Almeida Troncon
Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, School of Medicine of Ribeirão Preto, University of São Paulo, Ribeirão Preto, Brazila
- Corresponding Author:
- School of Medicine of Ribeirão PretoUniversity of São PauloE-mail:
Accepted Date: January 18, 2018
Citation: Ferreira SDC, Oliveira BBMD, Morsoletto AM, et al. Extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease: Clinical aspects and pathogenesis. J Gastroenterol Dig Dis. 2018 3:4-11.
Visit for more related articles at
Is Ulcerative Colitis Curable
Currently, theres no nonsurgical cure for UC. Treatments for the inflammatory disease aim to extend periods of remission and make flare-ups less severe.
For people with severe UC, curative surgery is a treatment option. Removing the entire large intestine will end the symptoms of UC.
This procedure requires your doctor to create a pouch on the outside of your body where waste can empty. This pouch can become inflamed and cause side effects.
For that reason, some people choose to have only a partial colectomy. In this surgery, your doctor only removes the parts of the colon that are affected by UC.
While these surgeries can help ease or end symptoms of UC, they can have adverse effects and possible long-term complications. Read more about these issues to determine if surgery is an option for you.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
IBD is a complex disease with widespread systemic manifestations that can present as a challenge to healthcare professionals. As such, it requires the efforts of an interprofessional healthcare team comprised of clinicians , specialists, nursing staff, and pharmacists. When these various disciplines coordinate their activities, exercise open communication, and function as a cohesive interprofessional team, patient outcomes will benefit.
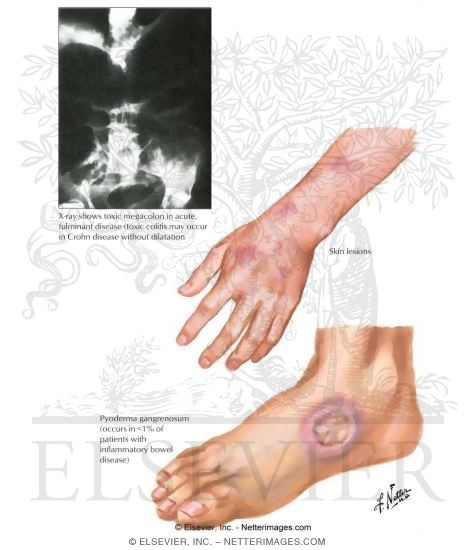
Several EIMs do not respond to intestinal-IBD treatment and hence require close monitoring and management to avoid complications. Musculoskeletal manifestations of IBD, including axial arthropathies, require frequent monitoring and coordinated management by gastroenterologists and rheumatologists. Regardless of being an ulcer, pyoderma gangrenosum has been known to worsen following surgical debridement due to pathergy. It is imperative to rule out pyoderma gangrenosum as the cause of an ulcer in IBD patients before proceeding. Additionally, pyoderma gangrenosum may require topical treatment by a dermatologist.
Recommended Reading: Low Dose Naltrexone Ulcerative Colitis
Plan Your Family Goals
Ulcerative Colitis usually doesnt affect the chances of getting pregnant. But many women have fewer children due to the fear that the disease could be passed on the child. Even though UC doesnt interfere in the pregnancy, it is important to plan it carefully. It is because, if a woman conceives during a flare, theres a high chance that the symptoms could worsen throughout the pregnancy.
Also Check: Can You Drink Alcohol With Ulcerative Colitis
Living With Uc: Probiotics
These friendly bacteria are similar to those that live in your intestine and prevent the growth of too many harmful bacteria. We need more research to know if probiotics can help with ulcerative colitis. You can find probiotics in some yogurts, milk, tempeh, and soy beverages. Or you can buy them as supplements.
Also Check: Causes Of Bleeding Ulcers In Stomach
You May Like: Best Medicine For Ulcerative Colitis
Ways To Reduce The Risk Of An Ulcerative Colitis Emergency
While many patients with ulcerative colitis may experience only mild or occasional symptoms, emergency situations can develop suddenly in both the newly diagnosed and in people who have had ulcerative colitis for a long time.
Keep in mind that the duration of flare-ups can be unpredictable and that remissions can vary in length, which means you always need to be on alert for any new or different symptoms.
The most important control patients have to prevent flare-ups is to continue their maintenance medications, as directed, says Hanauer. Antibiotics can also trigger flares, so they should only be used when appropriate not for colds or viral infections. Quitting smoking can also trigger flare-ups, so patients should discuss smoking cessation with their gastroenterologists.
Hanauer also recommends that patients with ulcerative colitis eat a healthy diet when theyre in remission to help ensure theyre meeting their nutritional requirements.
As the caregiver, youre in a unique position to notice changes in the nature and intensity of your loved ones ulcerative colitis symptoms. Always contact their medical team if you have any questions or suspect that the person with ulcerative colitis is experiencing an emergency. Your prompt action could save a life.
Additional reporting by Jordan M. Davidson.
Information Sources And Search Strategy
We will systematically search PubMed, Web of Science, MEDLINE, CINAHL, the Cochrane Library, Embase, China National Knowledge Infrastructure , Chinese Biomedical Literature database , and WANFANG database for related randomized controlled trials that compared one TCM intervention with another or with 5-ASA in the treatment of mild-to-moderate UC. The temporal interval is limited from the time that the databases created to February 2019.
The searches were restricted to papers that were published in English or Chinese. The search strategy will be conducted independently by 2 authors who are experienced in the information retrieval and combine free text words and medical subject headings regarding Chinese medicine,traditional Chinese medicine,Chinese herbal,Ulcerative colitis, UC,Inflammatory bowel disease,IBD, and randomized controlled trials. MeSH and subheadings were combined with AND or OR. Furthermore, we will also retrieve the WHO International Clinical Trials Registry Platform and ClinicalTrials.gov to identify ongoing trial registers. We will manually search related systematic reviews/meta-analyses and bibliographies of included studies to identify additional potential studies. The preliminary search strategy for PubMed is summarized in Table Table1,1, which will be adapted according to syntax-related requirements of other electronic databases.
You May Like: What Does A Stomach Ulcer Look Like
Recommended Reading: What Foods To Eat When You Have A Stomach Ulcer
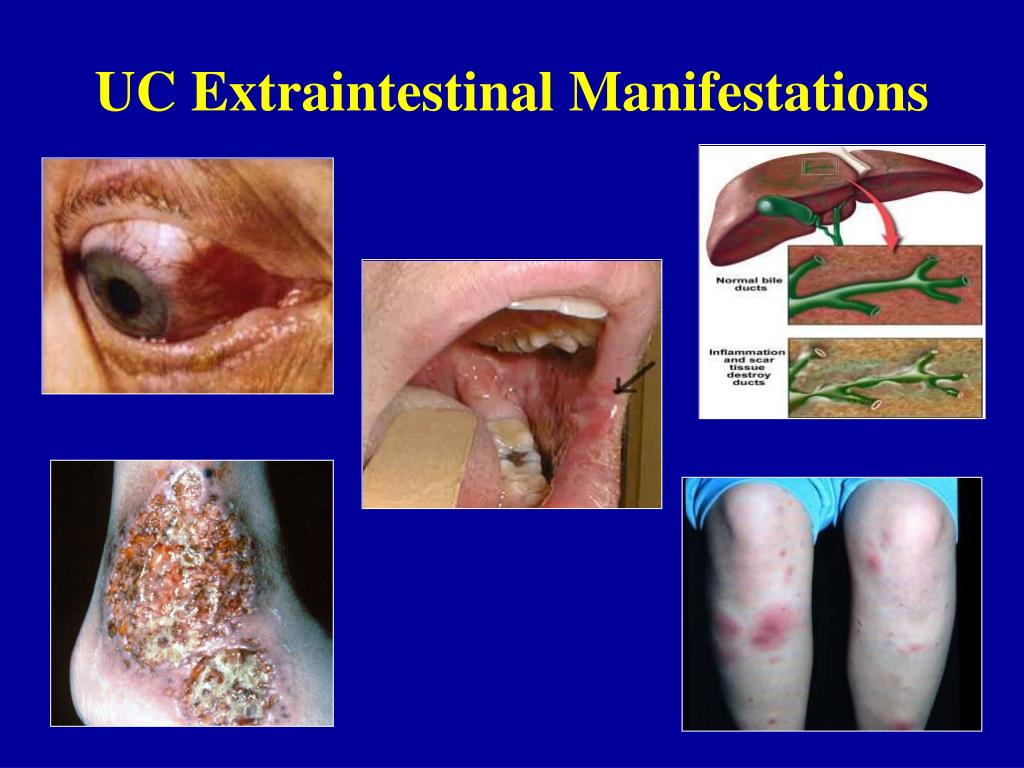
Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Extraintestinal Manifestations
Extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease can complicate treatment regimens and reduce patient quality of life. An understanding of the clinical presentations and treatment options for this disease may aid in improving patient outcomes, according to an article published in Gastroenterology.
Unlike extraintestinal complications of IBD, EIMs are not a sequela of intestinal inflammation, and may present before or after the development of gastrointestinal symptoms. Evidence suggests the likelihood of developing EIMs is tied to genetic variants and smoking. The presence of EIMs is common in both ulcerative colitis and Crohn disease. The relationship between EIMs and immune system response, as well as microbiota, is hypothesized but requires more research.
Musculoskeletal EIMs, affecting up to 46% of patients with IBD, are the most prevalent type. Categorized within the spondyloarthritis family, there may be axial or peripheral involvement. Treatment of the underlying IBD often improves musculoskeletal EIMs, though symptoms may persist despite adequate control of intestinal inflammation.
Cutaneous, ocular, and hepatobiliary EIMs are present in up to 15%, 7%, and 5%, of patients with IBD, respectively. Episcleritis, a common ocular EIM, is closely tied to intestinal inflammation and treatment of the underlying IBD is key. Other manifestations, such as the cutaneous EIM pyoderma gangrenosum, require treatment independent of IBD control.
Reference
What Are The Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis With Constipation
Thereâs no agreed-upon definition for UC with constipation. But a group of experts came up with a set of guidelines to better pinpoint it. In general, youâll need to have at least two of the following symptoms for at least 3 days a month during the prior 3 months:
- Bloating
- A sensation that you canât get all your stool out
Constipation may also cause:
- A sick feeling in your stomach
- Fatigue
The above symptoms can lead to other health issues, especially if you strain really hard when you poop. You may get:
- Tears or sores in the lining of your anus
- Swollen blood vessels around your anus
- Hard stool that gets stuck in your rectum
You May Like: Symptoms Of Having Ulcers In Your Stomach
Deterrence And Patient Education
EIMs of IBD should be differentiated from extraintestinal complications resulting from chronic inflammation associated with IBD resulting in nutritional deficiencies, osteopenia, osteoporosis, renal and gall stones, peripheral neuropathies, and IBD drug-associated side effects. Caution should be exercised when using Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in managing intestinal-IBD-related EIMs as they have been associated with IBD exacerbation.
As IBD increases the risk for bone loss and hypocalcemia, Primary care providers must counsel patients regarding the benefits of smoking cessation, physical activity, calcium, and vitamin D supplementation in their diet. IBD patients may be susceptible to thromboembolic events during prolong periods of immobility such as long-haul flights and need to take necessary precautions, including adequate hydration, smoking cessation, regular physical activity, and use of compression stockings.
The Difference In Extraintestinal Manifestations Of Inflammatory Bowel Disease For Children And Adults
Hyo-Jeong Jang1, Ben Kang2, Byung-Ho Choe2
1Department of Pediatrics, Keimyung University School of Medicine , 2Department of Pediatrics, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University , South Korea
Contributions: Conception and design: All authors Administrative support: All authors Provision of study materials or patients: All authors Collection and assembly of data: All authors Data analysis and interpretation: HJ Jang, B Kang Manuscript writing: All authors Final approval of manuscript: All authors.
Correspondence to:
Abstract: Extraintestinal manifestations are frequently observed in adult and pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease . The most common EIMs involve the joints, skin, and eyes, but they can affect various organs and result in significant morbidity. Since EIMs can appear years before the diagnosis of IBD is made, clinicians should be aware of their various manifestations to help decrease diagnostic delay of IBD and establish appropriate treatment plans.
Keywords: Inflammatory bowel disease extraintestinal manifestations pediatric Crohns disease ulcerative colitis
Submitted Dec 22, 2018. Accepted for publication Jan 23, 2019.
doi: 10.21037/tp.2019.01.06
Table 1Table 2
Also Check: Alternative Treatments For Ulcerative Colitis
What Are The Extraintestinal Manifestations Of Ulcerative Colitis
Benjamin Cohen, M.D., a gastroenterologist at Cleveland Clinic in Ohio, shares the various ways this disease can affect the body beyond GI distress.
Ulcerative colitis might be best known for its gut symptoms, but there are many ways it can affect a patient, from fatigue to low mood to joint pain. We talked with our experts during this live event to find out what people can do about extraintestinal manifestations of UC.
There are a number of different manifestations. The most common are usually the inflammatory arthritides. So, it can be peripheral arthritis, or you can have an axial arthritis. The challenge is that sometimes these these extra intestinal symptoms dont track with the disease itself. For example, your inflammation could be controlled, yet you could still have some of these extra intestinal symptoms.
This is an area of growing research, and were trying to understand more about how best to effectively treat both them. There are various skin conditions. There was a question about pyoderma gangrenosum which can occur and the surgeons often wind up dealing with that when patients have an ostomy, because thats one of the complications that can occur. Anemia is in many ways an extra intestinal symptom of the disease. Patients can develop eye symptoms or uveitis. Thats why its important to take a full history from your patient to understand all the different ways that they may manifest complications from their ulcerative colitis.
Renal And Pulmonary Manifestations
Nephrolithiasis, obstructive uropathy, and fistulization of the urinary tract are relatively common EIMs, occurring in 623% of patients with IBD.35 Secondary amyloidosis is a rare systemic complication that involves the kidneys. Patients can present with proteinuria, renal failure, and uremia. Studies have shown a 3-fold increased risk in males and a 10-fold increased risk in CD patients .36 In the majority of patients, other EIMs develop concurrently. A diagnosis can be made with a liver, rectal, or renal biopsy. Expedient renal transplantation in recent years has improved survival, although the survival rate after 15 years remains only 60%.37
Finally, subclinical disturbances in lung function are common in IBD patients.37 Clinically significant disease is extremely rare. Chronic bronchitis, subglottic stenosis, bronchiectasis, and bronchiolitis have all been reported in association with IBD.38,39 These conditions can occur in nonsmokers and do not parallel bowel disease. Sulfasalazine and mesalamine can induce interstitial lung disease on rare occasions.
Don’t Miss: How To Manage Ulcerative Colitis Pain
Ulcerative Colitis In Children
According to one study of IBD in the United States, 1 in 1,299 children between ages 2 and 17 years old were affected by the condition in 2016. Crohns disease was twice as common as UC, and boys were more likely to have IBD than girls.
For children with IBD, a diagnosis is more likely after 10 years old.
UC symptoms in children are similar to symptoms in older individuals. Children may experience bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain and cramping, and fatigue.
In addition, they may experience issues compounded by the condition, such as:
- anemia due to blood loss
- malnutrition from poor eating
- unexplained weight loss
UC can have a significant effect on a childs life, especially if the condition isnt treated and managed properly. Treatments for children are more limited because of possible complications. For example, medicated enemas are rarely used as a treatment method in children.
However, children with UC may be prescribed medications that reduce inflammation and prevent immune system attacks on the colon. For some children, surgery may be necessary to manage symptoms.
If your child has been diagnosed with UC, its important that you work closely with their doctor to find treatments and lifestyle changes that can help. Check out these tips for parents and children dealing with UC.
Presentation Of Disease At Diagnosis
Several attempts have been made in the past few years to define clinical presentation of late-onset UC and to determine if this variant may be different from adult forms.
Compared with adult-onset UC, more frequent weight loss but less frequent rectal bleeding and systemic symptoms like fever have been reported in older populations with UC onset . In particular, UC onset in older patients requires a careful diagnostic work-up to differentiate between drug-induced colitis , segmental colitis associated with diverticular disease, ischemic or infectious colitis or even neoplastic disease , and this may lead to the significant diagnostic delay reported in late-onset disease . Concerning disease extension at diagnosis , in a meta-analysis from 2016, left-sided colitis prevails in older-onset disease . This finding was confirmed by subsequent studies , whereas in other studies, extensive colitis or proctitis were more frequent in late-onset UC. Some studies found significant differences for disease extension at diagnosis between adult- versus late-onset UC , whereas others did not find such differences . Taken together, Fig. 1 depicts the most important studies in the past decade concerning disease extension at diagnosis including, where available, the corresponding figure of adult-onset UC.
Table 1 Comparison of the main features of ulcerative colitis at diagnosis and follow-up over 5 years, between adulthood-onset and late-onset diseaseFig. 1
Don’t Miss: I Have Ulcerative Colitis And Diverticulitis
How Does Ibd Affect Other Parts Of The Body
IBD can also cause problems outside the gut. Some people with IBD develop conditions affecting the joints, eyes or skin. These can be known as extraintestinal manifestations and often occur during active disease, but they can develop before any signs of bowel disease or during times of remission. Many of these are not very common.
JOINTS
Inflammation of the joints, often known as arthritis, is a common complication of IBD.
It is most common in those with Crohns Colitis and also affects about one out of 10 people with UC.
The inflammation usually affects the large joints of the arms and legs, including the elbows, wrists, knees and ankles. Fluid collects in the joint space, causing painful swelling, although pain may occur without obvious swelling. Symptoms usually improve with treatment of intestinal symptoms, and there is generally no lasting damage to the joints. A few people develop swelling and pain in the smaller joints of the hands or feet. This may be longer lasting and persist even when the IBD is in remission.
Sometimes, the joints in the spine and pelvis become inflamed a condition called ankylosing spondylitis . This can flare-up independently of IBD. It often causes pain over the sacroiliac joints, on either side of the lower part of the spine. Stiffness and pain in the spine itself may eventually lead to loss of flexibility.
SKIN
MOUTH
EYES
BONES
KIDNEYS
LIVER
Some complications are related to the liver and its function.
BLOOD CIRCULATION
ANEMIA
Prevalence Of Eims/comorbidities In Patients And Controls
In CD patients, the highest observed risks of EIMs were found among fistulas, OR 26.0 and OR 53.5 , anal and intestinal fistulas, respectively, . For the 21 diseases of special interest to our group, most were found to be of significant increased risk. Following fistulas, risks were highest for primary sclerosing cholangitis, ankylosing spondylitis, pyoderma gangrenosum, and erythema nodosum, in decreasing order. For prevalence of EIMs with significant risks, the highest were anal fistula , osteoporosis , psoriatic arthritis , pancreatitis , and psoriasis . The risk of colorectal cancer was only significant among CD diagnosed, 1.4% at OR 3.5 .
In UC patients, the highest observed risks of EIMs were found among Pyoderma gangrenosum, OR 16.1 and then psoriatic arthritis , and primary sclerosing cholangitis . Highest prevalence with higher significant risk is seen with osteoporosis , psoriatic arthritis , anal fistula , pancreatitis , and pulmonary embolism . Fistulas were observed to be of significant risk to UC patients for both anal and intestinal , as well as CD patients.
| . |
|---|
You May Like: How Does Ulcer Pain Feel
Time From Ibd Incidence To First Time Experiencing Eims/comorbidities
All patients who experienced EIMs/comorbidities were stratified according to time from CD/UC diagnosis to the first experience of each EIM/comorbidity . Among patients with the most common EIMs/comorbidities , 28%52% of CD patients and 37%53% of UC patients experienced these EIMs/comorbidities for the first time before their IBD diagnosis. Among patients who experienced EIMs/comorbidities in the metabolic system , 64%75% experienced this class of comorbidities for the first time before their IBD diagnosis. For the comorbidities not found before the IBD diagnosis, a trend is observed of experiencing them within the first year and then spread out over the follow-up years.
Time From Diagnosis to First EIM/Comorbidity by Diagnosis Class, Among Patients With CD and UC in Denmark
| . |
|---|
In Supplementary Table 2, an analysis similar to and is included, but with patients on biologics indicated for CD or UC compared with incident patients not treated with biologics in the period. For patients with first EIM coming before IBD diagnosis, being treated with biologics at some point tend to present with a decreased frequency of the EIM. For patients with EIMs coming after IBD diagnosis, the tendency of prevalence seems to be the reversed for some systems, especially the skin and intestinal tract systems, and the musculoskeletal systems for both CD and UC.