Is Pmh A Colitis
PMH is significant for ulcerative colitis diagnosed in college and treated with sulfazine for a few years. On review of her medical history, her last flare was almost 10 years ago and was resolved with cortisone enemas. She was advised to schedule a colonoscopy at that time but did not return until today.
Study Design Subjects And Data Sources
We first identified potential participants through the Ottawa Hospital Data Warehouse, a repository of hospitalizations, emergency department visits, day surgery visits and investigations occurring at The Ottawa Hospital. The Ottawa Hospital is a tertiary care hospital and IBD referral center, serving a population of more than 1.2 million people across Eastern Ontario. We identified all adult patients with one or more hospital encounters associated with a diagnosis of Crohns disease , 9th Version code 555.x or ICD 10th Version code K50.x ), UC , noninfective gastroenteritis and colitis, unspecified or indeterminate colitis and at least one lower endoscopic examination between April 1, 2001 and March 31, 2012, as potential participants.
We tested multiple administrative variables as candidate predictors in our regression models . These predictors were chosen based on having reasonable construct validity for measuring UC disease extent and activity by three IBD experts . Predictive models were separately developed for disease activity, disease extent and total disease burden and disease activity , stratified at various levels for each measure .
Table 1 Administrative variables tested in multivariable models
You Have A Disease In Which The Large Intestine Is Repeatedly Becoming Inflamed
The large intestine is like an upside down U in the abdomen. The first part lies in the lower right corner of the abdomen. Then it continues upwards and runs across from right to left. Then it descends again. There then follows an S-shaped part located on the bottom left side of the abdomen, which then merges into the rectum. The rectum is the last section of the large intestine .
You have ulcerative colitis. With this disease, the large intestine becomes repeatedly inflamed. The precise cause of this disorder is unknown.
The large intestine can be inflamed to a greater or lesser degree of severity. The large intestine may be permanently inflamed or suffer bouts of inflammation. As a result, the symptoms may have a greater or lesser degree of severity. It may also be that the large intestine has not been inflamed for a considerable time.
The disorder may cause a variety of symptoms. You may have bloody diarrhea, weight loss or abdominal pain, for example. It is also possible that you will have bleeding from your intestines.
With the disease, other areas of the body outside of the large intestine may also be affected. For example, the joints or skin may also become inflamed.
Recommended Reading: Does Aleve Cause Stomach Ulcers
How Do You Code Ulcerative Colitis
K51.911 Ulcerative colitis, unspecified with rectal bleeding.K51.912 Ulcerative colitis, unspecified with intestinal obstruction.K51.913 Ulcerative colitis, unspecified with fistula.K51.914 Ulcerative colitis, unspecified with abscess.K51.918 Ulcerative colitis, unspecified with other complication.More items…
Hydration Electrolytes And Nutritional Status
In addition to corticosteroids to reduce inflammation, most patients need intravenous fluids. These treat dehydration and correct electrolyte imbalance due to severe diarrhea, vomiting, and bleeding. Patients are at most risk for hypokalemia and iron deficiency anemia. In some cases, enteral nutrition support may also be helpful.
Recommended Reading: Signs I Have An Ulcer
Roles Of The Medical Home
- Monitor for signs of ongoing disease and exacerbation.
- Monitor for side effects of medications.
- Help ensure adequate catch-up growth.
- Monitor for appropriate pubertal development.
- Screen for physical findings of vitamin and mineral deficiencies.
- Screen for comorbid depression and anxiety.
- Evaluate illnesses in patients on immune-modulating medications.
- Work with the patient and family to encourage therapeutic compliance.
- Perform routine health screening and immunizations.
- Assist family in establishing care with a behavioral therapist.
- Assist family with eventual transition to adult care.
Is Ulcerative Colitis Chronic
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease in which abnormal reactions of the immune system cause inflammation and ulcers on the inner lining of your large intestine. Ulcerative colitis can develop at any age, but the disease is more likely to develop in people between the ages of 15 and 30.
Don’t Miss: Icd 10 Stage 3 Pressure Ulcer Sacrum
Diagnosis And When To Contact A Doctor
When diagnosing pancolitis, the doctor will ask the individual about their symptoms, general health, and medical history.
The doctor might also conduct a physical examination. This may involve them taking stool and blood samples to check for signs of infection and inflammation, among other things.
If the doctor is concerned that a person may have any form of inflammatory bowel disease, they may refer the individual for further tests, including:
- Blood tests: These can help when looking for cell counts and inflammatory markers.
- X-ray or CT scan: These can help rule out serious complications within the abdomen if there are other concerning signs or symptoms.
- Colonoscopy: In this procedure, the technician uses a flexible tube containing a camera, called a colonoscope, to examine the colon. During a colonoscopy, the surgeon may take a biopsy. The colon needs emptying before a colonoscopy. The procedure takes around 30 minutes and may be uncomfortable.
Pearls & Alerts For Treatment & Management
Test for tuberculosis before use of biologic agents
Children should be tested for tuberculosis prior to receiving biologic agents , and they should be monitored for opportunistic infections.
Live virus vaccinations
Patients with IBD on immunosuppressive medications are considered to have secondary immunodeficiency due to treatments that can include human immune mediators like interleukins and colony-stimulating factors, immune modulators, and medicines like tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitors and anti-B cell agents. The CDC recommends that non-live and live vaccines be administered 2 or more weeks before initiating such therapies. Live vaccines should be withheld 3 months following such therapies, and both non-live and live vaccines should be withheld at least 6 months following therapy with anti-B cell agents. Risks and benefits should always be discussed with families of patients on immunosuppression therapy prior to administration of live vaccines, especially in the context of possible travel outside the United States.
Pneumonia vaccination
Children with IBD should be immunized with 2 doses of pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine in addition to pneumococcal conjugate vaccine .
COVID-19 vaccination
The COVID vaccinations are safe and effective for patients with IBD, and patients should follow CDC guidelines on immunization booster schedule for immunosuppressed individuals, as their antibody response to vaccines may be altered by their medications.
Surgical emergencies
Read Also: What Do Venous Leg Ulcers Look Like
Icd 10 Diagnosis Code For Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis. K51 is a non-billable ICD-10 code for Ulcerative colitis. It should not be used for HIPAA-covered transactions as a more specific code is available to choose from below.
K51diseases involving the gastrointestinal tract, namely the oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine and rectum, and the accessory organs of digestion, the liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
Is K51 A Reimbursement Code
K51 should not be used for reimbursement purposes as there are multiple codes below it that contain a greater level of detail. The 2021 edition of ICD-10-CM K51 became effective on October 1, 2020. This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K51 – other international versions of ICD-10 K51 may differ. Use Additional.
Also Check: What Does A Mouth Ulcer Look Like
How To Diagnose And Treat Ulcerative Colitis
- Blood or stool tests to look for blood loss or signs of infection, which can trigger an ulcerative proctitis flare.
- Flexible sigmoidoscopy, a procedure in which the rectum and lowest part of the colon are examined. …
- Colonoscopy, which allows the doctor to view the entire colon using a thin, flexible, lighted tube with an attached camera. …
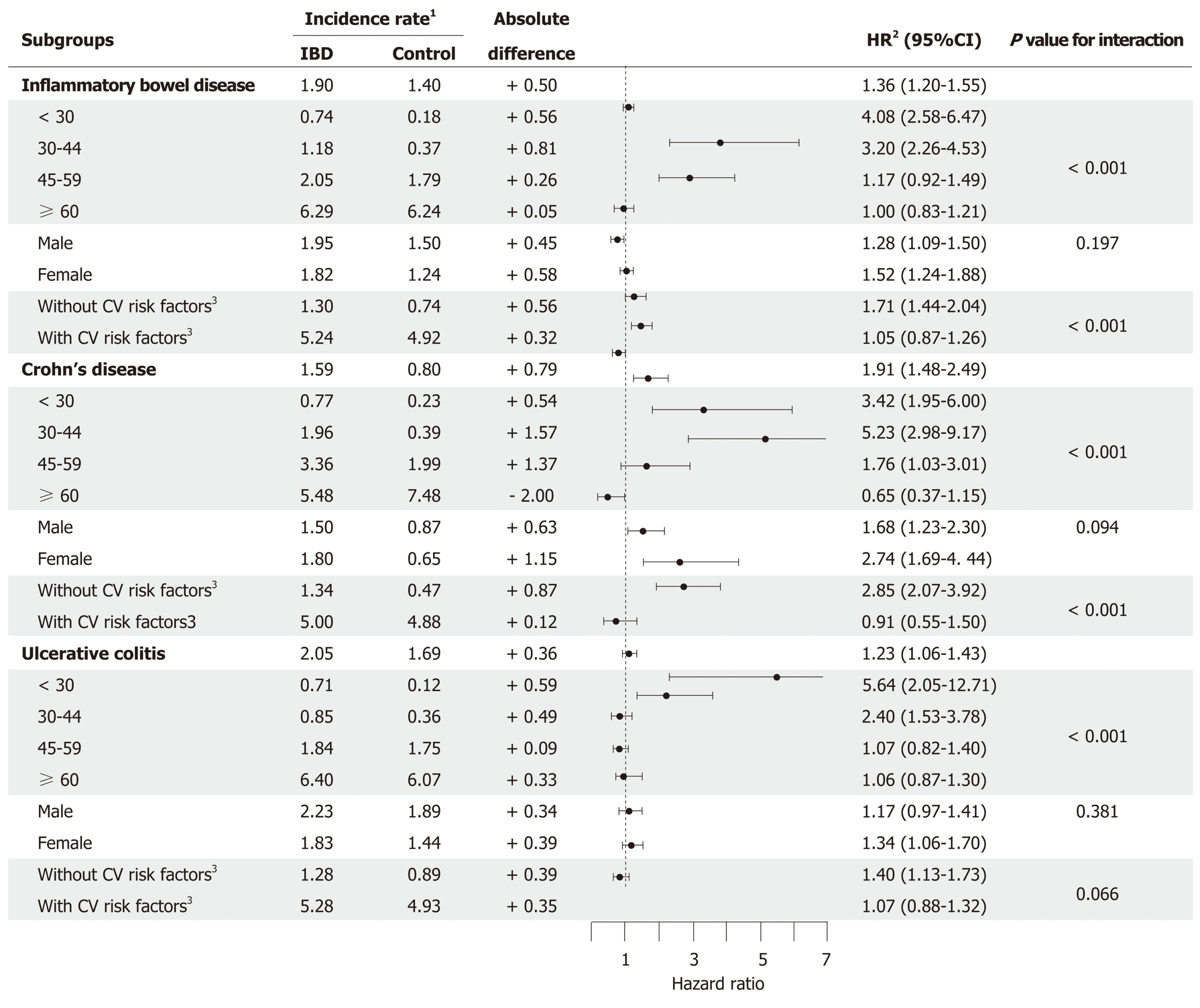
Is Colitis A Lethal Condition
Acute severe ulcerative colitis is a potentially lethalcondition that requires a pro-active approach with either effective medical treatment or timely colectomy. Although intravenous corticosteroids remain the first line treatment, in patients not responding after 35 days rescue medical therapy with either intravenous cyclosporine 2 mg/kg or infliximab 5 mg/kg IV should be considered …
You May Like: Ulcer On Eye From Contact Lens
How Is Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis Treated
ASUC is a challenging condition to treat. Once you’re admitted to the emergency room, you’ll get a series of tests, including blood tests, stool tests, and an exam of your bowel called a sigmoidoscopy. You’ll also get intravenous fluids to boost hydration.
The average hospital stay for ASUC treatment ranges from 4.6 to 12.5 days. During this time, your health care providers may include a gastroenterologist, colorectal surgeon, dietitian, pharmacist, and stomal therapist. The goal of hospitalizing you is to end the flare, get your symptoms under control, and put the disease into remission. Your doctors will want to make sure that rectal bleeding and diarrhea have stopped and normal bowel movements have returned. Rehospitalization is common.
Intravenous steroid medications are the most common treatment for ASUC. For 30% to 40% of ASUC patients, steroid treatments donât work â and taking steroid medications for more than 10 days increases your risk of complications.
If the steroids donât help within 3 to 5 days, your health care team will start âmedical rescue therapyâ with immunosuppressive drugs like cyclosporine or infliximab.
You might get an operation to remove part of your colon, called a colectomy, if your ASUC doesnât respond to steroids, immunosuppressants, or other medical treatments.
What Are Icd 10 Codes
Why ICD-10 codes are important
- The ICD-10 code system offers accurate and up-to-date procedure codes to improve health care cost and ensure fair reimbursement policies. …
- ICD-10-CM has been adopted internationally to facilitate implementation of quality health care as well as its comparison on a global scale.
- Compared to the previous version (i.e. …
You May Like: How Can You Prevent Pressure Ulcers
Ulcerative Colitis Unspecified Without Complications
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- K51.90 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM K51.90 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of K51.90 – other international versions of ICD-10 K51.90 may differ.
- Applicable To annotations, or
How Do Doctors Diagnose Ulcerative Colitis
What tests do doctors use to diagnose ulcerative colitis?
- Blood tests. A health care professional will take a blood sample from you and send the sample to a lab. …
- Stool tests. A health care professional will give you a container for catching and storing the stool. …
- Endoscopy of the large intestine. …
Recommended Reading: What Are Ulcers Caused From
Noninfective Gastroenteritis And Colitis Unspecified
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- infectious gastroenteritis and colitis NOS
- neonatal diarrhea
Reimbursement claims with a date of service on or after October 1, 2015 require the use of ICD-10-CM codes.
Diseases Of The Digestive Systemtype 2 Excludes
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
Type 1 Excludes
- Hemolytic anemia associated with ulcerative colitis
- Hemolytic anemia, with ulcerative colitis
- Mild chronic ulcerative colitis
- 385 Inflammatory bowel disease with mcc
- 386 Inflammatory bowel disease with cc
- 387 Inflammatory bowel disease without cc/mcc
Read Also: How To Know You Have A Ulcer
What Is Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis
Acute severe ulcerative colitis is a serious complication of ulcerative colitis. Itâs diagnosed when the disease flares and causes frequent bowel movements and bloody diarrhea, rapid heart rate, abdominal tenderness, fever, high levels of inflammation, and anemia. Inflammation in the intestinal wall makes the colon swollen and dilated, causing the stomach to become bloated. This is linked to a risk of developing toxic megacolon, the most serious complication of colitis.
ASUC is considered a medical emergency, and you’ll probably be hospitalized to help manage the disease. Without treatment, ASUC could be life-threatening.
What Is Pancolitis
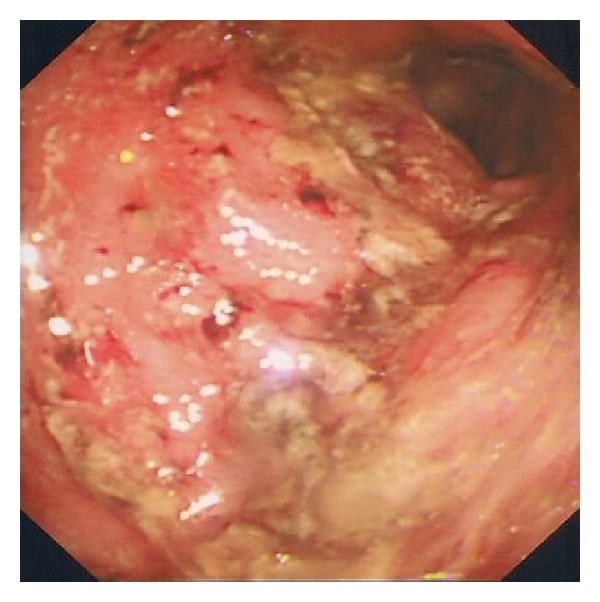
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the colon. At the end of the colon is the rectum, which stores feces before it leaves the body. In ulcerative colitis, small ulcers can develop on the colon, producing pus and mucus. In turn, this can lead to abdominal discomfort, diarrhea, and rectal bleeding.
When the inflammation covers the entire colon, doctors will diagnose a person with pancolitis.
Experts estimate that around 20% of people who have ulcerative colitis will have pancolitis.
Other types of ulcerative colitis include:
Don’t Miss: What Antiinflammatory Can I Take With Ulcerative Colitis
What Are The Long
The long-term outlook for ASUC is guarded. There is a 20% chance that you’ll need colectomy surgery after your first hospitalization, but that chance rises to 40% after two hospital admissions for ASUC. Severe flares are linked to a 1% risk of death.
Older age is linked with higher death rates. The death rate from ASUC is over 10% in people over 80 compared to fewer than 2% for people between the ages of 50 and 59.
UC is a chronic disease with no cure. Developing acute, severe symptoms is a risk for up to 20% of those diagnosed with the disease. With hospitalization, medical management, and a knowledgeable health care team, you can recover from a bout of ASUC and go into remission, but new flares are possible.
Show Sources
Who Is At Risk For Acute Severe Ulcerative Colitis
Most diagnoses of ulcerative colitis are in men between the ages of 15 and 35. The disease course for ASUC can be harder to predict, but it commonly appears between ages 34 and 48.
There is data showing that 54% of those who developed ASUC get it within 1 year of their UC diagnosis 18% developed ASUC within 1 to 5 years of their initial diagnosis and 28% were diagnosed with ASUC more than 5 years after their UC diagnosis.
Additional studies show that those who were diagnosed before the age of 40 had an aggressive disease course, had large or deep ulcers on their colons, higher levels of inflammation, were prescribed steroid medications earlier in their disease, and were at a higher risk of severe disease, including ASUC. Men were at higher risk of needing a colectomy than women.
Read Also: What Can I Take For Ulcerative Colitis
What Are The Treatment Options
Treatment for pancolitis will depend on how severe the condition is and how much the symptoms affect the persons life.
While there is no known cure, the two main aims of treatment are to reduce symptoms until they are gone, known as remission, and then to maintain remission.
The two types of treatment currently available are medication and surgery.
Does Colonoscopy Detect Colitis
You likely had a colonoscopy as part of your initial diagnosis of ulcerative colitis. A colonoscopy can help detect most ulcerative colitis cases, but it can miss some. A colonoscopy doesnt always see ulcerative colitis, especially if its in the upper or small intestine, because its harder to see that area during the exam.
Don’t Miss: Icd 10 Code For Ulcerative Colitis Unspecified
Is Ulcerative Proctitis The Same As Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative proctitis is a mild form of ulcerative colitis, a chronic inflammatory bowel disease consisting of fine ulcerations in the inner mucosal lining of the large intestine that do not penetrate the bowel muscle wall. There is a slightly increased risk for those who have a family member with the condition.