What Are The Signs & Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
The most common symptoms of ulcerative colitis are cramping belly pain and diarrhea. Other symptoms include:
- blood in the toilet, on toilet paper, or in the stool
- urgent need to poop
Ulcerative coliits can cause other problems, such as rashes, eye problems, joint pain and arthritis, and liver disease. Kids with ulcerative colitis may not grow well as well as other kids their age and puberty may happen later than normal.
What Causes Ulcerative Colitis Flareups
When youre in remission from ulcerative colitis, youll want to do everything you can to prevent a flareup. Things that may cause a flareup include:
- Emotional stress: Get at least seven hours of sleep a night, exercise regularly and find healthy ways to relieve stress, such as meditation.
- NSAID use: For pain relief or a fever, use acetaminophen instead of NSAIDs like Motrin® and Advil®.
- Antibiotics: Let your healthcare provider know if antibiotics trigger your symptoms.
When To Get Treatment
An increase in inflammation causes a flare, and the nature of inflammation means that you should treat it as quickly as you can. Inflammation grows exponentially, because inflammation itself causes an increase in inflammation. The longer you leave it untreated, the worse it will get. In addition, untreated inflammation not only leads to the symptoms associated with ulcerative colitis, it can also increase your risk of developing complications such as colorectal cancer down the line. Pay attention to your symptoms, and visit your physician if you notice that they change or increase even a small amount.
Read Also: Remicade Vs Humira Ulcerative Colitis
Disease Course Therapeutic Strategies And Complications
The use of mesalamine as a therapy for induction of remission was similar in the two groups , as well as steroid therapy and surgery . .
Table 2 UC therapeutic strategies, disease course and complications
Globally, surgery was performed more frequently in the elderly , with a mean time between diagnosis and surgery of 18.4months in the elderly and 24.87months in younger patients .
The type of surgery most frequently performed was partial colic resection , followed by perianal disease , colectomy and resection for cancer in the elderly colectomy and perianal disease in adults.
As maintenance therapy, there was no difference between the two groups in the use of mesalamine and immunosuppressant while biologic agents were much less used in the elderly .
During follow up, 57% of patients had at least one disease exacerbation, with a similar median time to first relapse . p 0.5615.
Extraintestinal manifestations were less common in the elderly , . Intestinal complications were more frequent in the elderly . In particular, stenosis was the most frequent complication in both groups. The other ones were toxic megacolon, intestinal perforation and haemoperitoneum.
Moreover, major infections were more common in the elderly . The most frequent infection was pneumonia in both groups . The other ones were sepsis , C. difficile infection for the elderly and CMV infection for the adults . Herpes Zoster infection and systemic candidiasis were also reported.
Ulcerative Colitis Questions To Ask Your Doctor
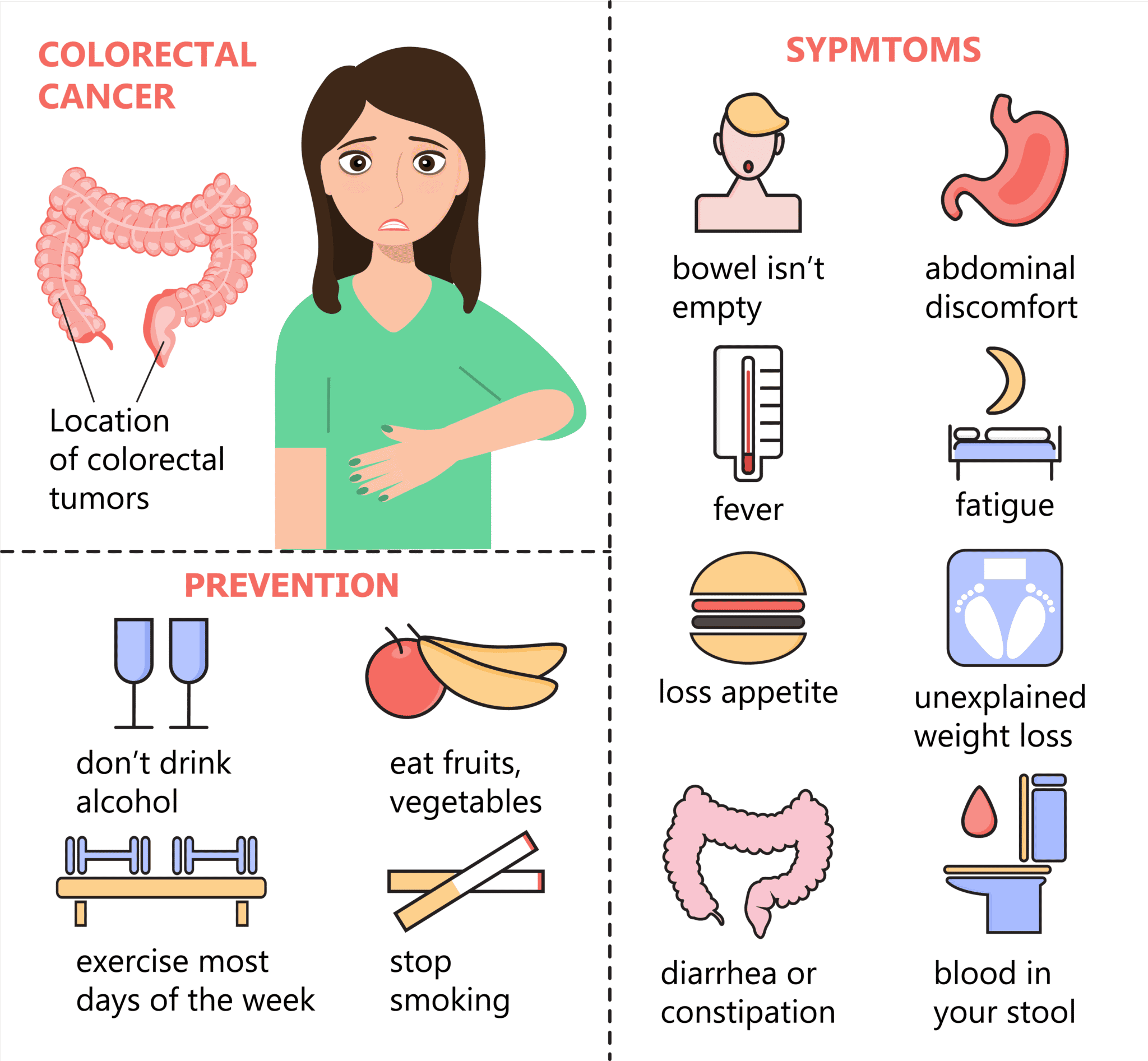
Whether youâre worried your symptoms are UC, or you already have the condition and want more information, here are questions to ask your doctor:
- Are my symptoms a sign of ulcerative colitis or another condition?
- Are there different kinds of UC? Do they have different symptoms?
- What tests will I need?
- If I have ulcerative colitis, what will my treatment plan be?
- Will changing my diet or lifestyle help ease my symptoms?
- How serious is my ulcerative colitis?
- If I take medication for ulcerative colitis, will there be side effects?
- Should I take nutritional supplements like probiotics?
- How often will I need to come in for checkups?
- What should I do if my symptoms suddenly get worse?
- How do I know if my ulcerative colitis is getting worse?
- How do I know if I should change my ulcerative colitis medication?
- Should I consider surgery? What does surgery involve?
- What is my risk of getting colon cancer?
You May Like: Can An Ulcer Cause Stomach Pain
Ulcerative Colitis: Treatment And Therapy
The cause of the inflammatory bowel disease ulcerative colitis is not yet known. Therefore, the goal of treatment is to alleviate the symptoms as well as to prolong the symptom-free phases.
Various drugs are used for this purpose: 5-aminosalicylic acid is an anti-inflammatory agent that is prescribed in the form of the precursor mesalazine as tablets, suppositories, foams or enemas. Corticosteroids also have an anti-inflammatory effect and are used either as suppositories, enemas or tablets. Both medications containing the active ingredient mesalazine and cortisone can cause severe side effects. Cortisone in particular can cause long-term side effects.
In severe cases or when cortisone is not effective, some patients receive immunosuppressants . This can have a positive effect on the course of the disease. However, TNF antibodies , which inhibit the inflammatory messenger TNF, can also be considered. When taking immunosuppressants and TNF antibodies, severe side effects such as susceptibility to infections can also occur, and poisoning is also possible.
Which drugs are used in treatment always depends on various factors, such as the extent of the symptoms and how far the inflammation has spread in the intestine, among other factors.
In addition to drug therapy, it is important for those affected to ensure a varied and balanced diet and to avoid hard-to-digest food components and hot spices during an acute episode.
Also Check: Natural Way To Cure Ulcer
What Does Ulcerative Colitis Look Like
With UC there is a wide variation in the amount of inflammation from person to person, so that in mild cases the bowel can look almost normal but, when the inflammation is bad, the bowel can look very red and ulcerated. Ulcerative colitis usually affects the rectum, but occasionally there is no inflammation . Sometimes the inflammation is limited just to the rectum . However, the inflammation can involve varying lengths of the colon. When the whole large bowel is affected, this is called pan-colitis .
Don’t Miss: Natural Cure For Stomach Ulcer
Crohns Disease And Ulcerative Colitis And Diet
Diet and food allergies do not cause IBD, and long-term special diets are not effective in treating IBD. However, adjusting your diet can help manage some of your symptoms, and can help IBD medications work better. A person with IBD has to pay close attention to their diet, since they may have malnutrition.
Surgery To Treat Ulcerative Colitis
Even with proper medication and diet, some children require surgery to attain the best possible quality of life. The decision to proceed with surgery is made in collaboration between the child and family, the gastroenterologist, and the surgeon specializing in IBD. Surgery is used to relieve severe, ongoing symptoms and to help children achieve growth and weight gain when medical management is no longer effective on its own. Unlike Crohns disease, in which surgery is a temporary solution, surgery can provide long-term relief with ulcerative colitis.There are multiple surgical options for the treatment of ulcerative colitis. At the Center for Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease, our team will work closely with your family to determine if surgery is necessary, and our expert surgeons who specialize in IBD-related procedures will provide additional information and work to optimize your childs quality of life. Learn more about J-pouch Surgery and Bowel Resection Surgery.
Don’t Miss: Wound Vac For Pressure Ulcers
Disability Benefits For Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is evaluated under the disability listing for inflammatory bowel disease in Social Security’s listing of impairments . To qualify under the IBD listing, you need to have a diagnosis of IBD, plus a specific complication such as anemia, a bowel obstruction, perineal disease with an abscess or fistula, or a tender abdominal mass. Or, if you have lost a significant amount of weight, you can qualify under the SSA’s disability listing for weight loss, which requires a BMI of 17.5 or less.
If you don’t have one of the requisite complications or amount of weight loss, you can also qualify for disability benefits if you can show that your symptoms make it impossible to do full-time work. For instance, if your diarrhea requires frequent and unplanned trips to the restroom, or your fatigue and anemia prevent you from working at an acceptable pace, the SSA may agree that you are unabe to work. For more information, see our section on how Social Security evaluates your ability to work.
You could be eligible for up to $3,148 per month in SSDI benefits
Treatment Of Ibd Complications
Treatment depends on the particular complication, but may include:
- complications caused by nutritional deficiencies vitamin and mineral supplements , changes to diet or a liquid diet in severe cases
- inflammation in other body areas usually ease when the bowel inflammation is controlled with medication
- fistulas small openings that often heal by themselves, with treatment to ease the inflammation. A person may need surgery to close a larger fistula. Abscesses may need antibiotics and surgical drainage
- intestinal obstruction in some cases, medical treatment to ease the inflammation will clear the obstruction. In severe cases, the person will need surgery
- toxic megacolon the person goes to hospital, and receives fluids and nutrients intravenously instead of by mouth, plus antibiotics and steroids to reduce inflammation. Sometimes, the doctor will remove the contents of the persons stomach with a slender tube . A ruptured bowel needs surgical repair or removal. In severe cases, the whole of the large bowel may need to be surgically removed.
Also Check: Things To Eat When You Have An Ulcer
Goals Of Ulcerative Colitis Treatment
At the IBD Center, our goals for treating your childs ulcerative colitis are to:
- Restore balance and health to your childs body
- Relieve any pain or other symptoms caused by ulcerative colitis
- Make sure your child is getting good nutrition
- Restore your childs growth and development
- Ensure your child builds the best bone density
- Help your child and family with the mental, emotional and social effects of IBD
Study Variables And Statistics

We studied and compared patients with CD and UC, regarding the following variables: follow-up demographic characteristics and clinical data .
Descriptive analysis included absolute and relative frequencies for categorical variables. Quantitative continuous variables with normal distribution were described as means and standard deviations. For those whose normality could not be determined, we described as medians with the first and third quartiles . To compare quantitative variables of normal unpaired distribution, Students t-test for independent samples for two groups was utilized. For unpaired samples that did not assume a normal distribution, the MannWhitney test was used for two groups and one-way ANOVA for comparisons between three groups. To compare categorical variables, the chi-square test for independent samples and the equality of proportions test were performed when appropriate. Descriptive levels of p< 0.05 were considered significant.
Don’t Miss: Chicken Recipes For Ulcerative Colitis
Diagnosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
X-rays of the abdomen taken after barium is given by enema do not require any special preparation . These x-rays usually can show a blockage or paralysis read more ) may indicate the severity and extent of the disease but are not done when the disease is active, such as during a flare-up, because of the risk of causing a perforation. Other x-rays of the abdomen may also be taken.
Extraintestinal Manifestations And Complications
UC is characterized by immune dysregulation and systemic inflammation, which may result in symptoms and complications outside the colon. Commonly affected organs include: eyes, joints, skin, and liver. The frequency of such extraintestinal manifestations has been reported as between 6 and 47%.
UC may affect the mouth. About 8% of individuals with UC develop oral manifestations. The two most common oral manifestations are aphthous stomatitis and angular cheilitis. Aphthous stomatitis is characterized by ulcers in the mouth, which are benign, noncontagious and often recurrent. Angular chelitis is characterized by redness at the corners of the mouth, which may include painful sores or breaks in the skin. Very rarely, benign pustules may occur in the mouth .
UC may affect the eyes. Inflammation may occur in the interior portion of the eye, leading to uveitis and iritis. Uveitis can cause blurred vision and eye pain, especially when exposed to light . Untreated, uveitis can lead to permanent vision loss. Inflammation may also involve the white part of the eye or the overlying connective tissue , causing conditions called scleritis and episcleritis. Uveitis and iritis are more commonly associated with ulcerative colitis, whereas episcleritis is more commonly associated with Crohn’s disease.
Don’t Miss: Remicade Vs Entyvio For Ulcerative Colitis
Care For Your Child Before And After Surgery
Before either surgery, your childs surgical team will explain the details, including:
- What will happen before, during and after your childs operation
- How long its likely to take
- How long your child may need to stay in the hospital afterward
- What kind of care your child will need at home after surgery
Some children who have pouch surgery have complications afterward. The IBD Center team provides care and support for these conditions, which include urgent need to use the bathroom, bleeding, inflammation of the pouch and problems emptying stool from the pouch. Treatment options offered through the IBD Center include dietary therapies, antibiotics, probiotics, medicines that reduce inflammation, treatments done with an endoscope and surgery.
The Link Between Ulcerative Colitis And Prostate Cancer
When Green learned that having UC puts him at increased risk for prostate cancer, it reinforced the importance of staying on top of his health.
Research shows that men with inflammatory bowel disease, particularly ulcerative colitis, may be at a higher risk of developing prostate cancer, with some studies showing an increased risk of up to 58%, Dr. Brandon Mahal, vice chair of research and assistant professor of radiation oncology at the University of Miami, told Healthline.
More research is needed to fully understand the connection, but one proposed explanation for the increased risk is that the chronic inflammation caused by UC contributes to the development of prostate cancer.
IBD is also known to have a genetic component, meaning that it can run in families. Some of the genes linked to IBD are also associated with prostate cancer, which may explain some of the association between the two conditions, Mahal said.
As one of the most common cancers among men, about 1 man in 8 will be diagnosed with the disease during his lifetime, according to the American Cancer Society .
Prostate cancer rarely occurs in men under 40 and about 60% of cases are diagnosed in men 65 or older. The disease is also more common in non-Hispanic Black men, reports the ACS.
Early detection of prostate cancer is crucial, said Dr. Ardeshir Rastinehad, vice chair of urology at Lenox Hill Hospital. He said screening and detection are easier and less intrusive than they once were.
You May Like: What Not To Eat When Having Ulcers
Iatrogenic Complications Adverse Drug Reactions And New Pathologies
Despite the similar use of steroid therapy in the two groups, iatrogenic complications were more common in the elderly . In particular, the most frequent ones were steroid diabetes and osteoporosis .
Unexpectedly, adverse drug reaction were less common in the elderly . . However, if we exclude patients on biological therapy, they were similar in the two groups . Globally, 10 adverse drug reactions developed in the elderly and 16 in the adult group, and the most frequent ones were skin reactions.
Fig. 3
During follow up, some conditions typical of old age were considered. A higher number of elderly patients developed cognitive impairment . Malignancy , deep vein thrombosis/pulmonary embolism , myocardial infarction , stroke and depression were also more frequent .
How To Stay Healthy
Keep up with treatment even when you’re in remission. That means you need to take your medicine even if you feel good. See your doctor at least once a year so they can see how things are going. And like everyone else, it’s important to stay active and follow a healthy diet.
Get regular screenings for colon cancer. Your doctor will let you know how often you should get checked. You may need a colonoscopy every 1-3 years. That’s a procedure that helps your doctor look for cancer or cells that might become dangerous. Your chances of recovery go way up when you find and treat colon cancer early.
Show Sources
Read Also: Over The Counter For Ulcerative Colitis
Will Ulcerative Colitis Affect Me Over Time
The effects of ulcerative colitis vary considerably from person to person, based on the nature and severity of their disease. In many cases, the condition does not have much impact on daily life, the ability to work or to enjoy an active social life but does take some getting used to. When it is at an active stage, symptoms such as diarrhoea and abdominal pain often require time away from work, college etc. and can make it difficult to cope going out or even being at home. However, treatment usually makes the symptoms better within days or weeks so normal quality of life can be restored quite quickly. Some severe cases of ulcerative colitis, however, can have a significant impact on peoples lives. This can be due to a weak response to treatment which makes symptom-free remission difficult to achieve and can involve frequent flare ups.
Ulcerative Colitis Causes And Risk Factors

Ulcerative colitis happens when your immune system makes a mistake. Normally, it attacks invaders in your body, like the common cold. But when you have UC, your immune system thinks food, good gut bacteria, and the cells that line your colon are the intruders. White blood cells that usually protect you attack the lining of your colon instead. They cause the inflammation and ulcers.
Doctors arenât sure why people get the condition. Your genes may play a role the disease sometimes runs in families. Other things in the world around you may make a difference, too.
Things that can affect your risk of getting ulcerative colitis include:
- Age. Itâs most likely if youâre between 15 and 30 years old or older than 60.
- Ethnicity. The risk is highest in people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent.
- Family history. Your risk could be up to 30% higher if you have a close relative with the condition.
Food and stress donât cause it, but they can trigger a flare of symptoms.
Read Also: What Can You Eat If You Have Ulcerative Colitis