Definition Of Clinical Outcomes
Our primary analysis was the comparison of the proportion of patients with clinical relapse in the MES 0 vs MES 1 group.
Clinical outcomes evaluated in our study included clinical relapse, IBD-related hospitalization rate, and colectomy. Clinical relapse was defined by disease activity scores and/or need for medication intensification .
Search Methods For Identification Of Studies
Electronic searches
We searched the following databases from inception to 5 July 2016:1. MEDLINE
The search strategies are reported in Appendix 1.
Searching other resources
We performed a manual review of bibliographies and abstracts submitted to major gastroenterology meetings including:
1. Digestive Disease Week 2. United European Gastroenterology Week and3. European Crohn’s and Colitis Organization.
Reference lists from retrieved articles were scanned to identify additional citations that may have been overlooked by the database search.
How To Calculate The Pucai Score
The PUCAI score ranges from 0 to 85 and is defined as:
- Remission : less than 10
- Predict the course of the disease over time
- Know when to recommend other treatments in severe cases
Experts recommend that doctors check a childâs PUCAI score during every visit and reevaluate treatment if their score is above 10.
Also Check: Skin Graft Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Definition And Current Concept Of Mucosal Healing
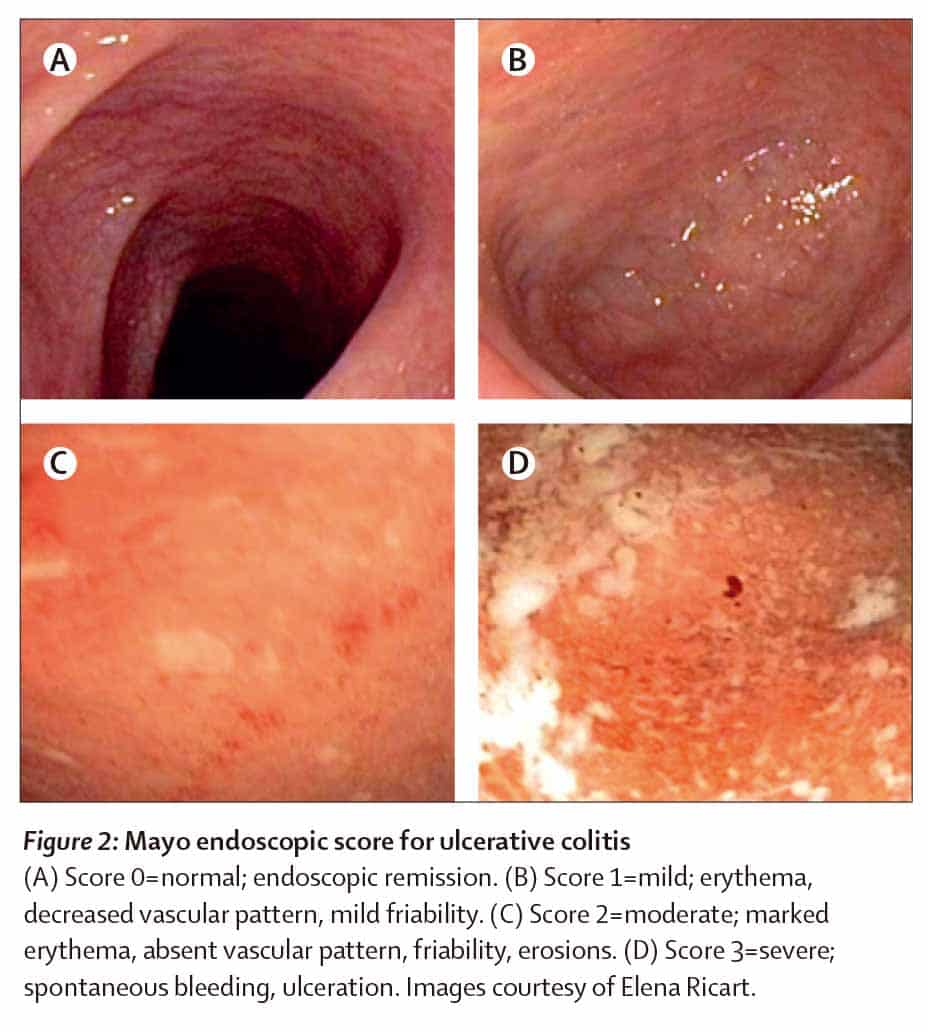
The definitions of mucosal healing have varied throughout recent medical literature, and there is currently no validated consensus on the matter. Mucosal healing has traditionally denoted the absence of visible ulcers on endoscopy, a definition that is more applicable to CD than UC, since the mucosa in UC often lacks ulcers . Another definition of mucosal healing, proposed by DHaens et al. , is endoscopic remission without blood, ulcers, erosions, or friability in each segment examined on endoscopy. Other definitions include improved endoscopic features, particularly in previously inflamed areas normal mucosa with pseudopolyps and histological healing . In trials of therapeutic agents, mucosal healing has been defined as a Mayo Endoscopic Subscore of 0 or 1 after therapy, in patients who scored 2 or more before .
Highlights In Ulcerative Colitis From The 17th Congress Of The European Crohns And Colitis Organisation: Commentary
The 17th Congress of the European Crohns and Colitis Organisation had been scheduled to take place in Vienna, Austria, but was reorganized as a virtual conference based on ongoing concerns about the COVID-19 pandemic. Many advances in the field were shared at the meeting. Here I discuss some of the clinically relevant abstracts about ulcerative colitis, which provided data for treatments such as ozanimod, Janus kinase inhibitors, and selective interleukin 23 inhibitors.
Ozanimod
Ozanimod is the newest available therapy for ulcerative colitis. Ozanimod is a first-in-class sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor modulator that is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis in adults.1 This mechanism is unique in the field of inflammatory bowel disease. Ozanimod is an oral small molecule that targets the signaling molecule S1P, and thereby blocks activated lymphocytes from trafficking through the lymphatic system to reach the inflamed bowel. S1P receptor modulators are also used to treat multiple sclerosis, and ozanimod is approved in this setting. At the 17th Congress of ECCO, several presentations provided efficacy and safety analyses of the pivotal phase 3 True North study of ozanimod.2
JAK Inhibitors
Selective IL-23 Inhibitors
Disclosure
References
4. Kinouchi Y, Hiwatashi N, Chida M, et al. Telomere shortening in the colonic mucosa of patients with ulcerative colitis. J Gastroenterol. 1998 33:343-348.
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Stomach Ulcer In Adults
Results Of Novel Clinical Study Of Guselkumab And Golimumab Combination Therapy Show Adults With Moderately To Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis Maintained Higher Rates Of Clinical Histologic And Endoscopic Remission At Week 38results Of Novel Clinical Study Of Guselkumab And Golimumab Combination Therapy Show Adults With Moderately To Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis Maintained Higher Rates Of Clinical Histologic And Endoscopic Remission At Week 38
The rate of clinical remission was 47.9 percent in patients who received combination induction therapy with guselkumab and golimumab compared with either treatment alone at 38 weeks1
SPRING HOUSE, PENNSYLVANIA, October 10, 2022 The Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson today announced data from an ongoing analysis of a Phase 2a clinical trial showing adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis who received 12 weeks of combination induction therapy with guselkumab and golimumab, followed by a transition to guselkumab alone for maintenance, achieved a clinical remission ratea b at week 38 of 47.9 percent, a higher rate than induction and maintenance treatment with either guselkumab alone or golimumab alone .1,2 Patients had comparable rates of adverse events across the treatment groups.1 Guselkumab alone, or the combination of guselkumab and golimumab are under clinical investigation and not approved for the treatment of adults with UC in the U.S.
The VEGA study is the first randomized controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of combination therapy with an interleukin -23p19 subunit antagonist and a tumor necrosis factor-alpha antagonist in UC.3,4 Detailed results were presented today as an oral presentation at the United European Gastroenterology Week 2022 congress taking place in-person in Vienna, Austria and virtually from October 8-11.1
Editors Notes:
h. Endoscopic remission is defined as an endoscopy subscore of 0.1
Risk Of Bias In Included Studies
Blinding
Blinding to clinical information such as symptoms, physical examination or laboratory information is important for the objective assessment of endoscopic data . However, the presence or absence of blinding was not routinely reported in the included studies.
Raters were blinded to clinical information in ten of the included studies . In one study, the endoscopic raters were not blinded to clinical information . It was unclear whether the raters were blinded to clinical information in the remaining nine studies .
Independent Observation
Eleven of the included studies did not assess interrater reliability , therefore observation by independent endoscopic raters was not relevant. Of the remaining eight included studies, independent observation was conducted in four instances . It was unclear whether independent observation was performed in the other five studies .
Read Also: Can Ulcerative Proctitis Be Cured
The Mayo Endoscopic Score Is A Novel Predictive Indicator For Malignant Transformation In Ulcerative Colitis: A Long
- 1Department of Colorectal Surgery, Xinhua Hospital, Shanghai Jiaotong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, Rui Jin Hospital, Affiliate to Shanghai Jiao Tong University, School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
Background: Data on the relative risk of malignant transformation in ulcerative colitis are insufficient. We investigated the potential value of the Mayo endoscopic score for predicting malignant transformation in patients with UC.
Methods: Data of patients with UC evaluated at our institute from June 1986 to December 2019 were retrospectively analyzed. The MES used in the study indicated the results of the first colonoscopy after hospitalization. We defined MES of 01 as low and MES of 23 as high. Univariable and multivariate logistic regression models were used for statistical analysis.
Results: Among the 280 eligible patients with UC with a median follow-up time of 14 years, those with a high MES were more likely to develop malignant transformation. High MES positively correlated with the degree of malignancy and was an independent risk factor for UC-associated dysplasia and colorectal cancer . Disease duration > 5 years , immunomodulator use , biologics nonuse , and Hb < 90 g/L were contributing factors for high MES.
Data Extraction And Assessment Of Studies Quality
Data extraction was carried out independently by two investigators . Any discrepancies were resolved by consensus in consultation with the senior authors .
Each reviewer extracted the following data: title and reference details , study population characteristics outcome data . All data were recorded independently by both literature reviewers in separate databases and were compared at the end of the reviewing process to limit selection bias. The database was then reviewed by a third person . Two authors independently assessed the quality of included studies using the NewcastleOttawa scale for casecontrol studies or cohort studies . Significant conflicts between NOS scores were resolved by consensus and consultation of senior authors , otherwise, scores were averaged between the two reviewers. Criteria evaluated for assesment of the quality of the included studies are reported in Additional file : Table S4. NOS scores were defined as high , moderate , or low .
Don’t Miss: Nanda Nursing Diagnosis For Ulcerative Colitis
Implication For Methodological Research
While three indices have undergone extensive validation, none of these instruments are fully validated and only two studies assessed responsiveness. Further research on the operating properties of these indices is needed given the lack of a fullyvalidated endoscopic scoring instrument for the evaluation of disease activity in ulcerative colitis.
Subgroup Analysis And Sensitive Analysis
A subgroup analysis was performed comparing studies with follow-up periods less than 12 months with those greater than 12 months.Moreover, we performed a subgroup analysis of studies including patients on conventional therapy, biological therapy, or both.
Sensitivity analysis was also conducted excluding the abstracts and the studies with low-moderate quality assessed by the New Castle-Ottawa scale . Moreover, a sensitivity analysis of studies that included only clinical relapse defined by Partial Mayo Score and among the studies with a prospective design was performed.
Don’t Miss: Do Ulcers Make You Throw Up
The Ulcerative Colitis Endoscopic Index Of Severity
The Ulcerative Colitis Endoscopic Index of Severity is a newer endoscopic scoring system that includes an assessment of vascular pattern, bleeding, and ulcers and excludes mucosal friability. In this system, the vascular pattern is rated as 13 with 1 as normal, 2 as patchy loss of vascular pattern, and 3 as complete loss of vascular pattern . Bleeding is characterized from 14 with 1 as none, mucosal bleeding as 2, mild colonic luminal bleeding as 3, and moderate or severe luminal bleeding as 4 . Erosions and ulcers are characterized from 14 with 1 as none, 2 as erosions, 3 as superficial ulcerations, and 4 as deep ulcers .
The Efficacy And Safety Of Guselkumab Induction Therapy In Patients With Moderately To Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Phase 2b Quasar Study Results Through Week 12
The randomized, double-blind phase 2b QUASAR Induction Study 1 evaluated the safety and efficacy of 12 weeks of guselkumab in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis.1 The trial enrolled patients previously treated with conventional or advanced therapy that was intolerable or inadequate. Their Mayo rectal bleeding score was 1 or higher at baseline and their Mayo endoscopy subscore was at least 2, based on central review. The patients were randomly assigned to receive placebo, guselkumab at 200 mg every 4 weeks, or guselkumab at 400 mg every 4 weeks. The primary endpoint was the clinical response at week 12.
Among the entire study population of 313 patients, the median age was 41.6±14.40 years, and 59.1% were male. The mean duration of ulcerative colitis was 7.55±6.79 years. The mean Mayo score was 9.2±1.32, and the mean modified Mayo score was 7.0±1.0. Seventy percent of patients had a modified Mayo score of 7, 8, or 9, and 70% of patients had an endoscopy subscore of 3, indicating severe disease. Medications in use at baseline included oral aminosalicylates , oral corticosteroids , and immunosuppressants , and 23.3% of patients were intolerant to 2 or more classes of advanced therapy.
Reference
1. Dignass A, Rubin DT, Bressler B, et al. The efficacy and safety of guselkumab induction therapy in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis: phase 2b QUASAR study results through week 12 . J Crohns Colitis. 2022 16.
Recommended Reading: Coconut Milk Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Why It Is Important To Do This Review
Increasing importance has been placed on the use of endoscopic indices as outcome measures in clinical research as these indices may function as a more objective measure of disease activity compared to symptombased indices. However, the operating properties of these endoscopic indices need to be clearly defined. In particular, an endoscopic index must be valid , responsive and reliable . Furthermore, an ideal instrument is feasible for use in clinical trials. This review will evaluate the relative merits of the existing endoscopic scoring indices and identify areas where further research is needed.
The Effects Of Maintenance Therapy With Upadacitinib On Abdominal Pain Bowel Urgency And Fatigue In Patients With Moderately To Severely Active Ulcerative Colitis: Phase 3 U
Upadacitinib is a reversible, selective Janus kinase inhibitor.1 In the phase 3 U-ACHIEVE and U-ACCOMPLISH trials, induction therapy with upadacitinib was superior to placebo in patients with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis who required treatment after previous therapy.2,3 Improvements were reported in symptoms such as abdominal pain, bowel urgency, and fatigue, which can be debilitating to these patients.4
Patients who demonstrated a clinical response during the 8-week induction period with daily upadacitinib were enrolled in the U-ACHIEVE maintenance trial. Silvio Danese, MD, PhD, presented results for this cohort.5This study randomly assigned 451 patients to receive upadacitinib at 15 mg, upadacitinib at 30 mg, or placebo, in a double-blind manner. Patient-reported outcomes of abdominal pain and bowel urgency were assessed during maintenance treatment. The Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy Fatigue instrument was used to measure fatigue. A change of 5 or more points from baseline in the FACIT-F score was considered a meaningful within-person change, and an increase of 40 or more points was considered normalization of fatigue.
References
1. Kim JW, Kim SY. The era of Janus kinase inhibitors for inflammatory bowel disease treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 22 :11322.
2. Sandborn WJ, Ghosh S, Panes J, et al. Efficacy of upadacitinib in a randomized trial of patients with active ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 2020 158:2139-2149.e14.
Read Also: Ulcerative Colitis And Lactose Intolerance
Additional File : Table S1
Research strategy. Table S2 Clinical outcomes and measures. Table S3 Baseline characteristics of the included studies. Table S4 Quality Assessment of Studies by Newcastle-Ottawa Scale. Table S5 Full text excluded. Fig. S1 Sensitivity analysis after abstract exclusion. Fig. S2 Sensitivity analysis after low-moderate quality studies exclusion. Fig. S3 Sensitivity analysis after abstract38 exclusion. Fig. S4 Sensitivity analysis after abstract41 exclusion. Fig. S5 Sensitivity analysis including studies with clinical relapse assessed with Partial Mayo Score evaluation. Fig. S6 Sensitivity analysis after retrospective studies exclusion. Fig. S7 Funnel plot for clinical relapse Eggers test: p = 0.47.
Overall Completeness And Applicability Of Evidence
Three endoscopic scoring indices, the UCCIS, UCEIS and Mayo Clinic Endoscopic Subscore, have undergone the most validation testing. The UCCIS has been evaluated for reliability , criterion validity and construct validity, while the UCEIS and the Mayo Clinic Endoscopic Subscore have been evaluated for reliability , construct validity and responsiveness. None of the currently available endoscopic scoring indices for ulcerative colitis have been fully validated .
Read Also: Honey Dressings For Leg Ulcers
Sensitivity Analysis And Publication Bias
Sensitivity analysis was conducted excluding the abstracts and the studies with low-moderate quality assessed at NOS. Both analyses showed a lower risk of clinical relapse for the MES 0 group. .
After the exclusion of each abstract separately , the results were , respectively .
Furthermore, sensitivity analysis was conducted with studies that included only clinical relapse defined by Partial Mayo Score . Among these studies, the MES 0 had a lower risk of clinical relapse compared to MES 1 .
A lower rate of clinical relapse was also observed in MES 0 group after the exclusion of studies with a retrospective design .
The asymmetrical shape of the funnel plot and the Eggers test showed no publication bias among studies analyzing the risk of clinical relapse .
Table : Ulcerative Colitis Endoscopic Index Of Severity
| Category |
|---|
- d) superficial ulcerations
- e) deep ulcerations
The so-called Baron Score classifies mucosal changes into 3 grades: 0=normal mucosa 1=inflammatory changes without bleeding 2=bleeding with minimal endoscopic manipulation 3=spontaneous bleeding . Remission is defined as Baron Score < /= 1.
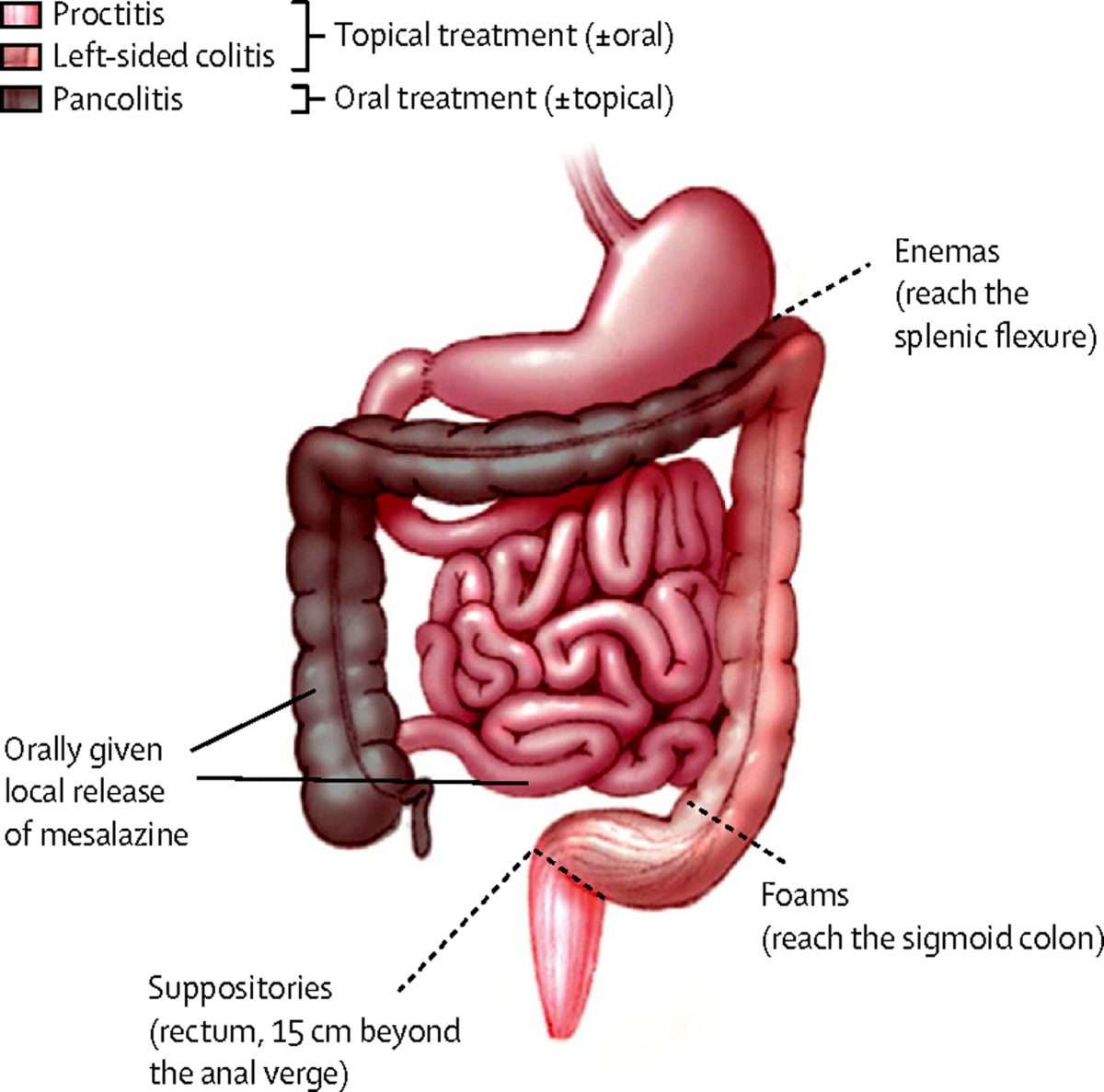
The so-called Mayo Score is a hybrid between clinical and endoscopic variables stool frequency, bleeding, inflammatory activity on sigmoidoscopy, overall physician assessment and daily activities of the patient are assessed . In studies, a decrease of the score by 3 or more is usually taken as therapeutic success. For the assessment of endoscopic mucosal response, the endoscopic subscore is most often used, and mucosal healing is diagnosed with an endoscopic subscore of 0 or 1 . It must also to be mentioned that the Mayo score was developed long before the advent of HD endoscopes, which are standard nowadays.
Also Check: Tnf Alpha Inhibitors For Ulcerative Colitis
Summary Of Main Results
In total, 23 reports of 20 studies that validated 19 different endoscopic scoring indices were identified by the literature search . Eighteen endoscopic scoring indices that have not undergone any form of validation testing were also identified . Correlation estimates for intrarater reliability for seven of the endoscopic scoring indices ranged from ‘moderate’ to ‘substantial’. Interrater reliability was assessed in nine of the partially validated indices, with correlation estimates ranging from ‘moderate’ to ‘almost perfect’ . Three of the included studies assessed criterion validity by calculating correlation estimates between an endoscopic scoring index and various biomarkers of inflammation . The effect size of the correlation estimates ranged from small to large . Twelve of the included studies explored construct validity by comparing a total of 13 endoscopic scoring indices with other measures of disease activity . The effect size of the correlation estimates ranged from small to large . Two of the included studies measured the responsiveness of a total of four endoscopic scoring indices . In Levesque 2014, effect size, Guyatt’s responsiveness statistic and area under the ROC ranged from 0.49 to 0.58, 0.32 to 0.47 and 0.66 to 0.68, respectively. In Ikeya 2016, the mean Mayo Clinic Endoscopic Subscore changed from 2.9 to 2.0 after tacrolimus therapy, while the mean UCEIS score changed from 6.2 to 3.4 .
Data Collection And Analysis
Two authors independently reviewed the studies identified from the literature search. These authors also independently extracted and recorded data on the number of patients enrolled number of patients per treatment arm patient characteristics including age and gender distribution endoscopic index and outcomes such as reliability , validity , responsiveness and feasibility. Any disagreements regarding study inclusion or data extraction were resolved by discussion and consensus with a third author. Risk of bias was assessed by determining whether assessors were blinded to clinical information and whether assessors scored the endoscopic index independently. We also assessed the methodological quality of the validation studies using the COSMIN checklist
You May Like: Remicade For Ulcerative Colitis Reviews