Who Can Get A Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Anyone who has diabetes can develop a foot ulcer. Native Americans, African Americans, Hispanics and older men are more likely to develop ulcers. People who use insulin are at a higher risk of developing a foot ulcer, as are patients with diabetes-related kidney, eye, and heart disease. Being overweight and using alcohol and tobacco also play a role in the development of foot ulcers.
Stem Cell Therapy For Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Diabetes mellitus prevalence has increased immensely due to worldwide changes in nutrition and lifestyle and is currently estimated to affect 425 million adults in 2017 and to increase to 629 million patients by 2045.
What is a Diabetic Foot Ulcer ?
Diabetic foot ulcers are among the most common complications of patients who have diabetes mellitus that is not well controlled. It is usually the result of poor glycemic control, underlying neuropathy, peripheral vascular disease, or poor foot care. It is also one of the most common causes of osteomyelitis of the foot and amputation of the lower extremities.
They are usually present in areas of the foot which encounter repetitive trauma and pressure sensations, with Staphylococcus being the most common infective organism.
Diabetic foot ulcers are responsible for more admissions than any other diabetic complication. Today, diabetes is the leading cause of non-traumatic amputations in the US. Overall, about 5% of patients with diabetes mellitus develop foot ulcers and 1% end up with an amputation.
What Causes Diabetic Foot Ulcers?
The etiology is multifactorial. The common underlying causes are poor glycemic control, calluses, foot deformities, improper foot care, ill-fitting footwear, underlying peripheral neuropathy, and poor circulation.
About 60% of diabetics develop neuropathy and eventually can lead to a foot ulcer. The risk is increased in individuals with a flat foot as they have disproportionate stress across the foot.
What Is A Diabetic Foot Ulcer
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound that occurs in approximately 15 percent of patients with diabetes, and is commonly located on the bottom of the foot. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, six percent will be hospitalized due to infection or other ulcer-related complication.
Diabetes is the leading cause of nontraumatic lower extremity amputations in the United States, and approximately 14 to 24 percent of patients with diabetes who develop a foot ulcer have an amputation. Research, however, has shown that the development of a foot ulcer is preventable.
Read Also: How Do You Treat A Duodenal Ulcer
New Diabetic Foot Ulcer Guidelines Highlight Importance Of Nutrition
New guidelines recommend healthcare providers develop and implement an individualized nutrition care plan for individuals with diabetes with or at risk of a DFU.
New guidelines endorsed by the American Limb Preservation Society highlighted the importance of nutrition in wound healing for adults with diabetes, who also experience diabetic foot ulcers .
The guidelines stated that nutritional interventions were recommended for all patients who could benefit now or in the future from nutritional care. As such, healthcare providers should develop and implement an individualized nutrition care plan for individuals with or at risk of a DFU, who are additionally malnourished or at risk of malnutrition.
DFUS are shown to develop in up to 34% of patients with diabetes at some point in their lives, with approximately 15% – 25% then requiring amputation. Previously, no internationally agreed upon standardized definition for malnutrition existed in the context of chronic wounds or in DFU.
Study author David G. Armstrong, DPM, MD, PhD, American Limb Preservation Society noted the new guidelines are designed to assist the clinician to “accomplish the difficult goal of improved outpatient nutrition to support the healing DFU wound.
Particularly, the guidelines stressed the importance of a multidisciplinary care team and how clinicians communicate with patients on the conceptualization of diabetes and its management, which may play a crucial role in treatment outcomes.
How Do Diabetic Foot Ulcers Form

Ulcers form due to a combination of factors, such as lack of feeling in the foot, poor circulation, foot deformities, irritation , and trauma, as well as duration of diabetes. Patients who have diabetes for many years can develop neuropathy, a reduced or complete lack of ability to feel pain in the feet due to nerve damage caused by elevated blood glucose levels over time. The nerve damage often can occur without pain and one may not even be aware of the problem. Your podiatric physician can test feet for neuropathy with a simple and painless tool called a monofilament.
Vascular disease can complicate a foot ulcer, reducing the bodys ability to heal and increasing the risk for an infection. Elevations in blood glucose can reduce the bodys ability to fight off a potential infection and also retard healing.
Don’t Miss: How To Cure Ulcer Naturally At Home In Tamil
Pearls And Other Issues
In summary, diabetic foot ulcers are precursors to amputations and require aggressive treatment. Patients should be screened for risk factors and referred for diabetic footwear when risk is identified. Staphylococcus aureus is the most important pathogen in diabetic foot infections, but as the depth and severity increase, these become polymicrobial. Surgery is indicated for the reversible peripheral vascular disease. Callouses should be debrided, and a moist wound healing environment should be maintained. Achille’s tendon lengthening combined with total contact casting speeds healing and decreases the likelihood of recurrence and hyperbaric oxygen therapy is indicated in selected cases to speed healing and prevent amputation.
Nutrition Can Aid In Healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers
We were unable to process your request. Please try again later. If you continue to have this issue please contact .
In this issue, Susan Weiner, MS, RDN, CDE, CDN, talks with nutrition and wound care expert Nancy Collins, PhD, RDN, LD, NWCC, FAND, about the role of nutrition in prevention and treatment of diabetic foot ulcers. Nutrition is a critical component of healing diabetic foot ulcers, particularly as it relates to immune function, malnutrition, glycemic control, and weight loss and weight maintenance. Diabetes educators should include nutrition assessment and intervention as key components of the overall diabetes treatment plan to help patients with diabetic foot ulcers maximize their nutritional status and promote wound healing.
Nutrition is not often the first thing clinicians think of when dealing with diabetic foot ulcers. How important is it, and exactly what role does nutrition play?
How does elevated blood glucose interfere with wound healing?
Collins: High blood glucose can lead to defective white blood cell function and make a diabetic foot ulcer susceptible to infection. It also can affect the production of inflammatory molecules, interfere with collagen synthesis and change cellular morphology. In a study of patients at the Johns Hopkins Wound Center, elevated HbA1c was significantly associated with poor wound healing.
Are there vitamins or supplements that can maximize the rate of healing?
How do these amino acids aid in wound healing?
Recommended Reading: Best Probiotic For Ulcerative Colitis
You Are What You Eat: How Nutrition Can Aid In Healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers
The Important Role of Nutrition in Wound Healing
Nutrition is a critical component of healing, particularly as it relates to immune function, glycemic control, malnutrition, and weight loss, as well as weight maintenance. Every visit to the wound clinic gives clinicians the opportunity to discuss nutrition with patients while providing treatment.
Nutrition intervention does not require anything fancy or complicated. Sometimes, all it takes is inquiring about what the patient ate that day or providing a list of healthy food suggestions. A more formal way to begin nutrition education is to ask patients to complete a nutritional screening questionnaire, such as the MNA® Mini Nutrition Assessment . This validated, six-question tool takes just a few minutes to complete and can identify those at risk for malnutrition, as well as those who are possibly already malnourished. Wound Care Advantage clinicians can find additional nutrition information in the companys Luvo operating system.
Malnutrition and/or nutrient deficiencies can impair collagen synthesis, prolong inflammation, decrease phagocytosis , and decrease the mechanical strength of the skin. For these reasons, it is important to ask patients about their food intake and help them understand the importance of eating a variety of nutrient-dense foods each day.
Providing Chairside Advice
Here are some easy answers to three of the most common questions asked by patients with diabetic foot ulcers.
What should I eat?
When To See Your Doctor
If you begin to see blackened flesh around an area of numbness, see your doctor right away to seek treatment for an infected foot ulcer. If untreated, ulcers can cause abscesses and spread to other areas on your feet and legs.
At this point, ulcers can often only be treated by surgery, amputation, or replacement of lost skin by synthetic skin substitutes.
Also Check: In Order To Prevent Pressure Ulcers
Extremely Accelerated Healing Of Diabetic Foot Ulcers With Medical Nutrition Therapy: Report Of The First Three Cases
Log in to MyKarger to check if you already have access to this content.
Buy a Karger Article Bundle and profit from a discount!
If you would like to redeem your KAB credit, please log in.
Save over 20%
- Rent for 48h to view
- Buy Cloud Access for unlimited viewing via different devices
- Synchronizing in the ReadCube Cloud
- Printing and saving restrictions apply
USD 8.50
- Access to all articles of the subscribed year guaranteed for 5 years
- Unlimited re-access via Subscriber Login or MyKarger
- Unrestricted printing, no saving restrictions for personal use
The final prices may differ from the prices shown due to specifics of VAT rules.
Guidelines On Healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers Emphasize Personalized Nutrition
14 Feb 2022 — Personalized nutrition can go a long way in helping individuals living with diabetic foot ulcers heal and prevent malnutrition, according to new guidelines published in the US.
The future in this area is really bright, as guidelines like this can move the needle in helping to ultimately hyper-personalize a nutrition plan for everyone, Dr. David Armstrong, co-author of the guidance, founding president of the American Limb Preservation Society and professor of surgery at the University of Southern California, tells NutritionInsight.
Developed by a team of medical professionals including a podiatrist, dietician and surgeons, the Nutrition Interventions in Adults with Diabetic Foot Ulcers are endorsed by the American Limb Preservation Society. The printing and distribution was supported by Abbott.
The guidelines bring the importance of nutrition front and center, recommending health care providers who work with diabetic patients to assess the risk of malnutrition and developing DFUs. With the information on hand, doctors should help patients implement an individualized nutrition care plan, he adds. Educating patients with DFUs about the best dietary sources of essential nutrients involved in wound healing can lead to improved outcomes.
Moderate or severe malnutrition has been identified in over half of patients with DFU, and malnutrition in DFU is correlated with increased lower extremity amputation, Armstrong highlights.
Don’t Miss: Air Mattress For Pressure Ulcer Prevention
Why It Is Important To Do This Review
Altering nutritional intake has been shown in studies to improve wound healing in other wound types . However, the precise role of nutrition in the treatment of foot ulcers in people with diabetes is as yet, unclear. Nutritional intervention may potentially improve clinical outcomes such as healing rates and healing times of foot ulcers in people with diabetes. The outcomes of this review may provide evidence to formulate such guidance, furthermore, this review may indicate areas for future research.
Manage Your Blood Glucose Levels
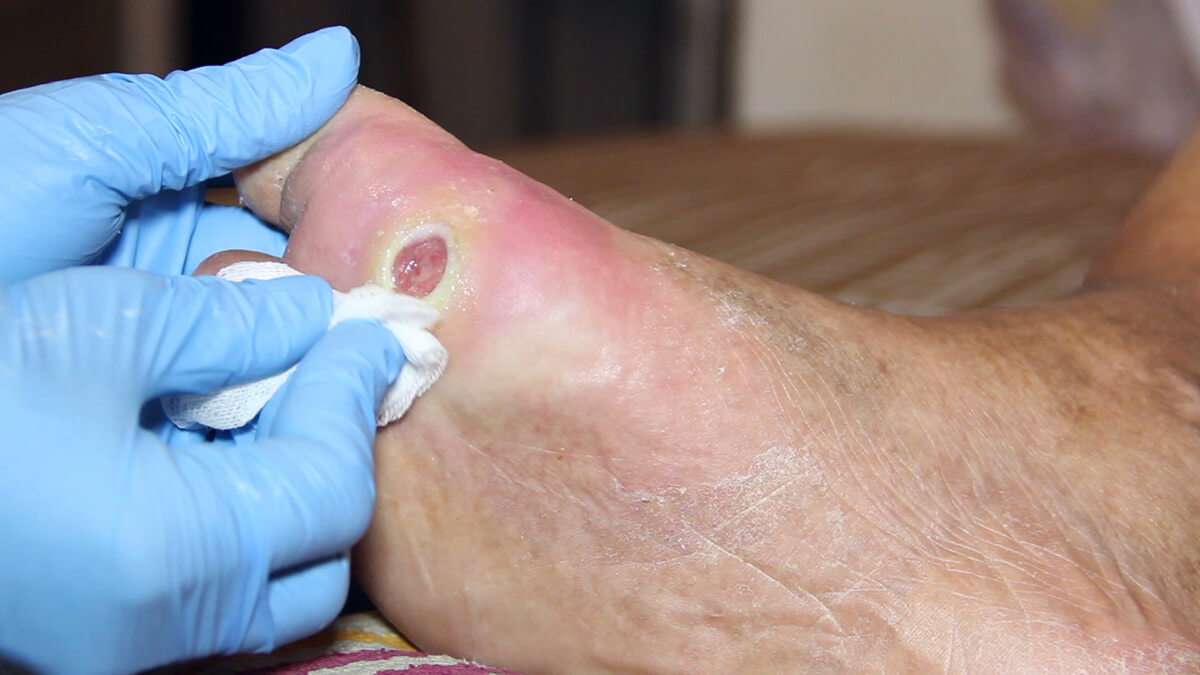
If youre able to keep your blood glucose at healthy levels, it may help you avoid some of the reasons why wounds dont heal in diabetics.
For one, it will help your circulation immensely. You will also be less likely to develop advanced neuropathy.
With healthy blood glucose levels, it should be much easier for your body to heal cuts and bruises, which may help prevent diabetic foot ulcers.
Of course, no plan is perfect, and for some people, diabetic foot ulcers are a way of life no matter how they try to prevent them. So how can a diabetic wound heal faster?
Well, by bringing the list here to your doctor and creating a treatment plan.
If you have regular DFUs, or have a wound that simply wont heal, then its important to learn and understand as much as you can about advanced diabetic wound healing products and supplements.
As a reminder, much of the wound healing process comes from within. And a supply of healthy foods and supplements will help give your body the resources it needs to fend off any illnesses, heal wounds faster, and prevent future ones.
Here at ProT Gold, we are an industry leader in creating medical-grade collagen products that are trusted in nearly 4,000 medical facilities across the United States. Our formula is easy to digest, contains no additives or excess sugars, and has already helped many people in their diabetes wound healing journey.
You May Like: Best Wound Care For Stage 2 Pressure Ulcer
How Can A Foot Ulcer Be Prevented
The best way to treat a diabetic foot ulcer is to prevent its development in the first place. Recommended guidelines include seeing a podiatrist on a regular basis. He or she can determine if you are at high risk for developing a foot ulcer and implement strategies for prevention.
You are at high risk if you:
- Have neuropathy
- Have a foot deformity
- Wear inappropriate shoes
- Have uncontrolled blood sugar
Reducing additional risk factors, such as smoking, drinking alcohol, high cholesterol, and elevated blood glucose are important in the prevention and treatment of a diabetic foot ulcer. Wearing the appropriate shoes and socks will go a long way in reducing risks. Your podiatric physician can provide guidance in selecting the proper shoes.
Learning how to check your feet is crucial in noticing a potential problem as early as possible. Inspect your feet every dayespecially between the toes and the solefor cuts, bruises, cracks, blisters, redness, ulcers, and any sign of abnormality. Each time you visit a health care provider, remove your shoes and socks so your feet can be examined. Any problems that are discovered should be reported to your podiatrist or a medical professional as soon as possible, no matter how simple it may seem to you.
The key to successful wound healing is regular podiatric medical care to ensure the following gold standard of care:
- Lowering blood sugar
How The Intervention Might Work
Nutritional status may be an important predictor of wound healing . The importance of nutrition in wound healing in general is well founded in the literature . Leininger 2002 states that the main goal of nutrition in wound healing is to provide optimum calories and nutrition to aid healing, however deficiencies in protein, albumin, vitamin D, vitamin C and zinc have all been demonstrated to decrease wound healing rates.
Hypomagnesemia , is thought to contribute to development of neuropathy and abnormal platelet activity , while the impact of vitamin D supplementations on wound healing arises due to its impact on stimulating phagocytosis and killing the bacteria by macrophages . Zinc contributes to the regulation of the different phases of wound healing including inflammation, angiogenesis and reepithelialisation . In addition, vitamin E has been shown to improve healing through regulation of inflammation, in experimental animal studies .
Recommended Reading: What Is The Recommended Diet For Horses With Ulcers
How Should A Diabetic Foot Ulcer Be Treated
The primary goal in the treatment of foot ulcers is to obtain healing as soon as possible. The faster the healing of the wound, the less chance for an infection.
There are several key factors in the appropriate treatment of a diabetic foot ulcer:
- Prevention of infection
- Taking the pressure off the area, called off-loading
- Removing dead skin and tissue, called debridement
- Applying medication or dressings to the ulcer
- Managing blood glucose and other health problems
Not all ulcers are infected however, if your podiatric physician diagnoses an infection, a treatment program of antibiotics, wound care, and possibly hospitalization will be necessary.
Preventing Infection
There are several important factors to keep an ulcer from becoming infected:
- Keep blood glucose levels under tight control
- Keep the ulcer clean and bandaged
- Cleanse the wound daily, using a wound dressing or bandage
- Do not walk barefoot
Off-Loading
For optimum healing, ulcers, especially those on the bottom of the foot, must be off-loaded. Patients may be asked to wear special footgear, or a brace, specialized castings, or use a wheelchair or crutches. These devices will reduce the pressure and irritation to the ulcer area and help to speed the healing process.
Applying Medication and Dressings
For a wound to heal there must be adequate circulation to the ulcerated area. Your podiatrist may order evaluation test such as noninvasive studies and or consult a vascular surgeon.
Managing Blood Glucose
Identifying Symptoms And Diagnosis
One of the first signs of a foot ulcer is drainage from your foot that might stain your socks or leak out in your shoe. Unusual swelling, irritation, redness, and odors from one or both feet are also common early symptoms.
The most visible sign of a serious foot ulcer is black tissue surrounding the ulcer. This forms because of an absence of healthy blood flow to the area around the ulcer.
Partial or complete gangrene, which refers to tissue death due to infections, can appear around the ulcer. In this case, odorous discharge, pain, and numbness can occur.
Signs of foot ulcers are not always obvious. Sometimes, you wont even show symptoms of ulcers until the ulcer has become infected.
Talk with your doctor if you begin to see any skin discoloration, especially tissue that has turned black, or feel any pain around an area that appears callused or irritated.
Your doctor will likely identify the seriousness of your ulcer on a scale of 0 to 5 using the Wagner Ulcer Classification System:
- 0: no open lesions may have healed lesion
- 1: superficial ulcer without penetration to deeper layers
- 2: deeper ulcer, reaching tendon, bone, or joint capsule
- 3: deeper tissues involved, with abscess, osteomyelitis, or tendonitis
- 4: gangrene in a portion of forefoot or heel
- 5: extensive gangrenous involvement of the entire foot
Ulcers in people with diabetes are most commonly caused by:
- poor circulation
- nerve damage
- irritated or wounded feet
Infection of a foot ulcer can be prevented with:
Don’t Miss: Horse Stomach Ulcers Natural Remedies