Pressure Ulcer Of Left Buttock Stage 3
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- L89.323 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L89.323 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L89.323 other international versions of ICD-10 L89.323 may differ.
- Healing pressure ulcer of left buttock, stage 3
- Pressure ulcer with full thickness skin loss involving damage or necrosis of subcutaneous tissue, left buttock
- Applicable To annotations, or
Read Also: Is Gluten Bad For Ulcerative Colitis
Pressure Ulcer Of Sacral Region
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
- Pressure ulcer of coccyx, unstageable
- Pressure ulcer of sacrum, unstageable
- Unstageable pressure ulcer of coccyx
- Unstageable pressure ulcer of sacrum
- 573 Skin graft for skin ulcer or cellulitis with mcc
- 574 Skin graft for skin ulcer or cellulitis with cc
- 575 Skin graft for skin ulcer or cellulitis without cc/mcc
- 592 Skin ulcers with mcc
- 593 Skin ulcers with cc
- 594 Skin ulcers without cc/mcc
Info For Medical Coders On How To Properly Use This Icd
- Inclusion Terms:
Inclusion Terms
Inclusion Terms are a list of concepts for which a specific code is used. The list of Inclusion Terms is useful for determining the correct code in some cases, but the list is not necessarily exhaustive.
- Healing pressure ulcer of sacral region, stage 4
- Pressure ulcer with necrosis of soft tissues through to underlying muscle, tendon, or bone, sacral region
Also Check: Crohn’s Disease And Ulcerative Colitis Differences
What Is Sacroiliac Dysfunction
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction occurs when the sacroiliac joints of the pelvis become stiff or weak. The condition can develop at any age. Symptoms typically are felt on one side of the back. SIJ dysfunction is found in 10% to 25% of people who complain of low back pain. It is most often diagnosed in females.
The Icd Code L89 Is Used To Code Pressure Ulcer
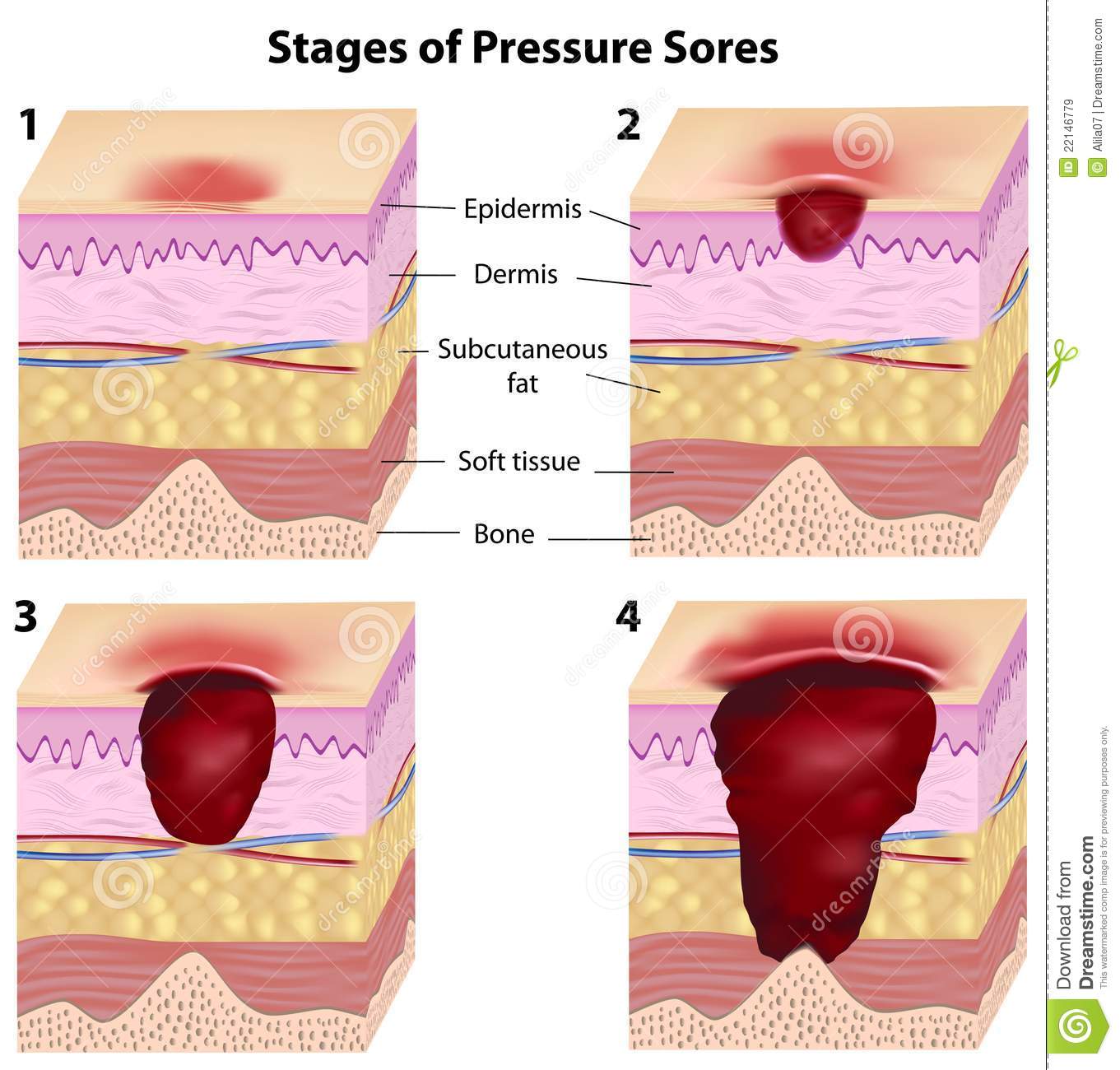
Pressure ulcers, also known as pressure sores, bedsores and decubitus ulcers, are localized injuries to the skin and/or underlying tissue that usually occur over a bony prominence as a result of pressure, or pressure in combination with shear and/or friction. The most common sites are the skin overlying the sacrum, coccyx, heels or the hips, but other sites such as the elbows, knees, ankles or the back of the cranium can be affected.
| Specialty: |
Don’t Miss: What Can I Do For Ulcer Pain
Pressure Ulcer Of Sacral Region Unspecified Stage
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- L89.159 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L89.159 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L89.159 – other international versions of ICD-10 L89.159 may differ.
- Healing pressure ulcer of sacral region NOS
- Healing pressure ulcer of sacral region, unspecified stage
- Applicable To annotations, or
What Are The 4 Stages Of A Pressure Ulcer
These are:Stage 1. The area looks red and feels warm to the touch. … Stage 2. The area looks more damaged and may have an open sore, scrape, or blister. … Stage 3. The area has a crater-like appearance due to damage below the skin’s surface.Stage 4. The area is severely damaged and a large wound is present.
You May Like: What Helps Ulcers In Your Mouth
Factors That Influence Sacral Ulcer Management
While wound management is a key part of sacral ulcer management, treating patients holistically is the key to success. Apart from ischemia, other factors that impede normal healing include poor nutrition, infection, edema, persistent moisture, fecal and urinary soiling, and shearing forces. One can look for, prevent, or minimize each of these risk factors. Of course, the patient should be frequently repositioned to avoid further tissue damage and to promote healing.
When selecting a dressing, the wound should be kept moist but not contain excessive amounts of exudate. Wound care professionals should consider the type of ulcer and any comorbid conditions that could complicate treatment . Arterial wounds generally require a moisture-retaining dressing, while wounds that arise from venous insufficiency usually require a dressing that absorbs excess moisture. All surfaces of the wound, including any tunnels, should be packed with the appropriate dressing.
Also Check: What To Avoid Eating If You Have An Ulcer
Diseases Of The Skin And Subcutaneous Tissuetype 2 Excludes
- 2016201720182019202020212022Non-Billable/Non-Specific Code
Code First
Recommended Reading: Low Sulfur Diet Ulcerative Colitis
Coding Tip: Reporting Pressure Ulcers
Kim Boy, RHIT, CDIP, CCS, CCS-P
This Coding Tip was updated on 07/12/22
The coding of pressure ulcers has seen many changes over the past several years. Coders have seen that ICD-10-CM also came with changes on reporting of these ulcers.
With ICD-10-CM, the code for reporting pressure ulcers now identifies the site and the stage of the ulcer. Pressure ulcer stages are based on severity of the ulcer:
- Unspecified stage and
If a patient has more than one pressure ulcer a code for each should be reported.
Sometimes, coders will confuse unstageable with unspecified stage of the ulcers. There is a big difference between the two meanings:
- Unstageable pressure ulcers are diagnosed when the physician or clinician is not able to stage due to the ulcer being covered by eschar or possibly even a skin graft. If a patient with an unstageable pressure ulcer has a debridement and the stage of the ulcer is then revealed and documented, only code the stage revealed and not unstageable.
- Unspecified pressure ulcers are reported with there is a lack of documentation regarding the pressure ulcer stage
There are only a few areas in coding where the coder is allowed to take documentation from anyone other than the physician. The staging of the pressure ulcer is one of those exceptions. Other clinicians can document the stage of an ulcer and coders may code from this documentation. However, the diagnosis of the ulcer itself must be documented by the physician/provider.
Tabular List Of Diseases And Injuries
The Tabular List of Diseases and Injuries is a list of ICD-10 codes, organized head to toe into chapters and sections with coding notes and guidance for inclusions, exclusions, descriptions and more. The following references are applicable to the code L89.153:
Inclusion Terms
- Healing pressure ulcer of sacral region, stage 3
- Pressure ulcer with full thickness skin loss involving damage or necrosis of subcutaneous tissue, sacral region
You May Like: Snack Ideas For Ulcerative Colitis
L895 Pressure Ulcer Of Ankle
Pressure ulcer of unspecified ankle
Pressure ulcer of right ankle
L898 Pressure Ulcer Of Other Site
Pressure ulcer of head
Pressure ulcer of other site
Recommended Reading: Ulcerative Colitis Flare Up Length
Pressure Ulcer Of Sacral Region Stage 4
- 2016201720182019202020212022Billable/Specific Code
- L89.154 is a billable/specific ICD-10-CM code that can be used to indicate a diagnosis for reimbursement purposes.
- The 2022 edition of ICD-10-CM L89.154 became effective on October 1, 2021.
- This is the American ICD-10-CM version of L89.154 other international versions of ICD-10 L89.154 may differ.
- Healing pressure ulcer of sacral region, stage 4
- Pressure ulcer with necrosis of soft tissues through to underlying muscle, tendon, or bone, sacral region
- Applicable To annotations, or
Pressure Ulcer And Non
Pressure ulcer and non-pressure chronic ulcer diagnostic codes are located in ICD-10-CM chapter 12, Disease of the skin and subcutaneous tissue. The concept of laterality is pertinant, and should be included in the clinical documentation for skin ulcers.ICD-10-CM codes for Pressure ulcers, located in Category L89, are combination codes that identify the site, stage, and the laterality of the ulcer. Possible stages are 1-4 and unstageable.
Stage 1: Skin changes limited to persistent focal edemaStage 2: An abrasion, blister, and partial thickness skin loss involving the dermis and epidermisStage 3: Full thickness skin loss involving damage and necrosis of subcutaneous tissueStage 4: Necrosis of soft tissues through the underlying muscle, tendon, or bone
Unstageable: Based on clinical documentation the stage cannot be determined clinically or for ulcers documented as deep tissue injury without evidence of trauma.An instructional note in ICD-10 states to code also any associated gangrene .Non-pressure chronic ulcers are similar to pressure ulcers in that they require documentation of the site, severity, and laterality. Category L97 and L98 are for Non-pressure ulcers, and have an instructional note to code first any associated underlying condition, such as:
Associated gangreneAtherosclerosis of the lower extremitiesChronic venous hypertensionThe severity of the ulcers is described as:Limited to breakdown of skinWith fat layer exposedWith necrosis of muscleWith necrosis of bone
Don’t Miss: Best Supplement For Gastric Ulcers In Horses
Pressure Ulcer Nursing Care Plans
A pressure ulcer is a localized skin injury where tissues are compressed between bony prominences and hard surfaces such as a mattress. They are caused by pressure in combination with friction, shearing forces, and moisture. The pressure compresses small blood vessels and leads to impaired tissue perfusion.
Pressure Ulcer Of Sacral Region Stage 4l89154
Chapter 12 – Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue » Other disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissue » Pressure ulcer of sacral region, stage 4
Hierarchy Tree View
YOU AGREE THAT THE INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE IS PROVIDED AS IS, WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF ANY THIRD-PARTY PATENT, COPYRIGHT, OR ANY OTHER THIRD-PARTY RIGHT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE CREATORS OF THE WEBSITE OR WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF OR IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE WEBSITE, THE USE OF THE WEBSITE, OR THIS AGREEMENT, WHETHER IN BREACH OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, EVEN IF SUCH PARTY IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Recommended Reading: Best Thing For Stomach Ulcers
Pressure Ulcer Icd 10 Causes
The three most important factors that contribute to bedsores are:
- Pressure: Ulcers are caused by pressure on the skin limiting blood flow to the skin. Constant pressure on any part of the body reduces blood flow to the tissues.
- Limited exercise: Lack of blood flow makes the skin more susceptible to damage that leads to the development of bedsores. Blood flow is crucial for supplying the tissue with oxygen and other nutrients. Without these nutrients, the skin and nearby tissues can be damaged and die.
- Friction: Friction occurs when the skin rubs against clothing or bed linen. Friction makes sensitive skin more susceptible to injury, especially when the skin is moist. Shearing occurs when two surfaces move in opposite directions. In people with reduced mobility, this type of pressure tends to occur in non-padded areas such as muscles, fat and low-lying bones such as the spine, coccyx, shoulder blades, hips, heels and elbows. For example, if the bed is lifted, the patients head slips onto the bed. When the tailbone moves, the skin around it stays in place but is pulled in the opposite direction. They are most common in bony parts of the body such as heels, elbows, hips and the base of the spine. They usually develop and form within a few hours.
Pressure Ulcer Of Sacral Region Stage 3l89153
Chapter 12 Diseases of the skin and subcutaneous tissue » Other disorders of the skin and subcutaneous tissue » Pressure ulcer of sacral region, stage 3
Hierarchy Tree View
YOU AGREE THAT THE INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE IS PROVIDED AS IS, WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING WITHOUT LIMITATION WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR ANY PARTICULAR PURPOSE, OR NON-INFRINGEMENT OF ANY THIRD-PARTY PATENT, COPYRIGHT, OR ANY OTHER THIRD-PARTY RIGHT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE CREATORS OF THE WEBSITE OR WASHINGTON UNIVERSITY BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF OR IN ANY WAY CONNECTED WITH THE WEBSITE, THE USE OF THE WEBSITE, OR THIS AGREEMENT, WHETHER IN BREACH OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, EVEN IF SUCH PARTY IS ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Also Check: What Is An Ulcer In Your Mouth
Don’t Miss: Nanda Nursing Diagnosis For Ulcerative Colitis
Symptoms Of Stage 3 And Stage 4 Pressure Ulcers
Stages 3 and 4 pressure ulcers have deeper involvement of underlying tissue with more extensive destruction. Stage 3 involves the full thickness of the skin and may extend into the subcutaneous tissue layer granulation tissue and epibole are often present. At this stage, there may be undermining and/or tunneling that makes the wound much larger than it may seem on the surface. Stage 4 pressure ulcers are the deepest, extending into the muscle, tendon, ligament, cartilage or even bone.
Figure 1: Stage 4 sacral pressure ulcerFigure 2: Stage 3 pressure ulcer on hip
Pressure Ulcer Icd 10 Treatment

Treatingpressure ulcer ICD 10 include:
- reducing the pressure on affected skin
- caring for the wound
- preventing infection
- keeping a good diet is needed
Members of the care team are a GP who supervises the treatment plan, a nurse who specialises in wound care, a nurse who provides care and training, and someone who administers the wound. Physicians specialized in skin diseases may also be involved. The nursing team may also include a social worker to help the patient and his family access resources and address emotional concerns related to long-term recovery, a physiotherapist to help improve mobility, an occupational therapist to ensure adequate seating and a nutritionist to monitor the patients nutritional needs and recommend good nutrition.
The following list contains numerous ways to treat and manage pressure ulcer ICD 10:
Recommended Reading: Signs Of Ulcers In Colon
L894 Pressure Ulcer Of Contiguous Site Of Back Buttock And Hip
Pressure ulcer of contiguous site of back, buttock and hip, unspecified stage
Pressure ulcer of contiguous site of back, buttock and hip, stage 1
Pressure ulcer of contiguous site of back, buttock and hip, stage 2
Pressure ulcer of contiguous site of back, buttock and hip, stage 3
Pressure ulcer of contiguous site of back, buttock and hip, stage 4
Pressure ulcer of contiguous site of back, buttock and hip, unstageable
Pressure-induced deep tissue damage of contiguous site of back, buttock and hip