What Are Arterial Ulcers
A condition called peripheral arterial disease can reduce blood flow to your extremities. When this happens, your foot tissue may start to die. The ulcers that form from reduced blood flow are called arterial ulcers.
The word arterial means relating to arteries. Arteries are blood vessels that transport blood from your heart to the rest of your body, including your feet and toes. Anyone can get an arterial ulcer, but people who smoke or have diabetes, high blood pressure or high cholesterol are at higher risk.
Unlike neurotrophic ulcers, arterial ulcers can form on many parts of your body, including:
- On the tips of your toes.
- Between your toes .
- The bony parts of your feet and toes that rub against bed sheets, socks or shoes.
Arterial ulcers are:
- An unusual walk that puts too much pressure on one part of your foot or toe.
- Friction when your foot or toe rubs against the toe box of your shoe.
Although they dont cause ulcers, foot and toe ulcers are often found alongside toe conditions such as hammertoe, mallet toe and claw toe.
Enhancing Healthcare Team Outcomes
Diabetes is a chronic disease that has a significant number of life-threatening complications, of which one of them is a foot ulcer. Diabetic foot is a common scenario in which healthcare workers will come across in daily practice. Besides a lack of blood flow, many patients with diabetes mellitus with a foot ulcer also have neuropathy for which there is no cure. The diagnosis and subsequent management of a diabetic ulcer are optimally effective when utilizing an interprofessional approach to achieve the best outcome.
Many patients with diabetes mellitus with a foot ulcer end up with amputations and become disabled. Thus, today the key is preventing the foot ulcer with education. The pharmacist, nurse practitioner, the primary care provider should educate the patient on the harms of smoking and the need for better control of blood glucose. In addition, patients with diabetes mellitus need to be taught about appropriate shoe wear, podiatric care, and control of hyperlipidemia. The team, including the diabetic nurse educator and clinicians, must work together toward educating the patient and family on preventative measures to minimize morbidity and improve outcomes.
Outcomes
Loss of a limb leads to enormous morbidity and many patients are not able to afford a prosthesis. Most remain disabled for life and lead a poor quality of life.
Wound Care And Dressings
Care for your wound as instructed by your provider. Other instructions may include:
- Keep your blood sugar level under good control. This helps you heal faster and helps your body fight infections.
- Keep the ulcer clean and bandaged.
- Cleanse the wound daily, using a wound dressing or bandage.
- Try to reduce pressure on the healing ulcer.
- Do not walk barefoot unless your provider tells you it is OK.
Read Also: Is Honey Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Prediabetes Symptoms Causes Treatment Options
Prediabetes is a condition that affects millions of people in the United States and it is defined as having a blood sugar level that is higher than normal, but not high enough to be diagnosed as diabetes. When you have prediabetes, it often leads to type 2 diabetes if it is not treated. In this article, we will discuss what prediabetes is, the symptoms of prediabetes, the causes of prediabetes, and the treatment options for prediabetes among other topics.
How To Prevent Diabetic Foot Ulcers
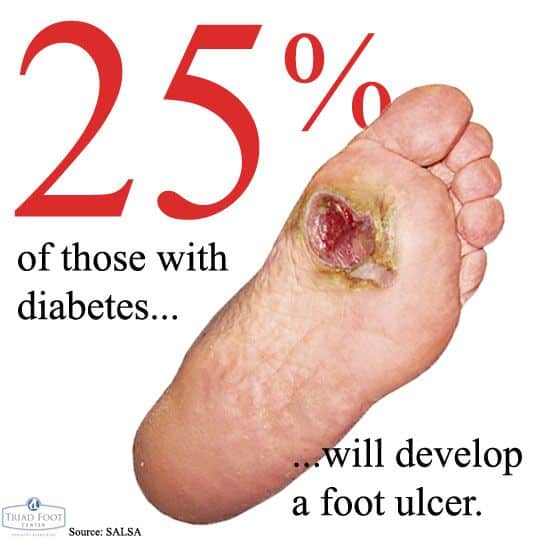
The first line of defense in preventing diabetic wounds is to follow the guidelines recommended to keep the disease itself under control:
- Maintain healthy blood sugar levels through a healthy diet and by taking medications as instructed by your doctor.
- Keep your blood pressure within a healthy range.
- Avoid alcohol and tobacco.
You should also take measures to avoid causing sores or wounds on the feet:
- Never walk barefoot.
- Wear shoes that fit properly and dont rub the skin.
- Wash your feet daily with mild soap and lukewarm water to prevent the buildup of bacteria on the skin, which can cause infection even in the tiniest skin breaks.
Because a loss of sensation in the feet may mean theres no pain felt even when an ulcer is present, its also extremely important for those with diabetes to regularly check for any foot sores or skin irritation. This way, the ulcer can be properly treated as early as possible.
Recommended Reading: Is Coconut Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Fructosamine To A1c: How Are They Related
Diabetes, also called diabetes mellitus, is a condition that affects millions of people all over the world. It can be difficult to manage, but with the right tools and information, it is possible to live a healthy life with diabetes. One of the most important tools for managing diabetes is understanding fructosamine levels and hemoglobin A1C levels. In this article, we will explain what fructosamine and hemoglobin A1C are, and discuss the relationship between these two measures. We will also provide tips on how to test your fructosamine and hemoglobin A1C levels correctly.
What Causes A Diabetic Foot Infection
Two main factors contribute to diabetic foot infections. The first is neuropathy, or nerve damage, that can significantly impair feeling in the legs and feet. The inability to feel pain means that people at risk for developing an infection may not feel a blister developing inside a sock, or possibly a pebble that has worked its way into a shoe. The person might not know to remove the source of friction or injury, which can lead to a laceration. This vulnerability allows potentially harmful bacteria to enter the body unnoticed.
Peripheral artery disease is another phenomenon that can cause diabetic foot infection. People with this condition have impaired blood flow, which can slow or prevent the healing of a small injury. This, in combination with not being able to feel the initial injury, can put diabetics at risk of developing moderate to severe foot infections.
Research also shows that heightened blood glucose, such as that experienced by diabetics, can impair white blood cells ability to navigate to an infection, expediting the infections development. Additionally, dry skin is a common experience for people with diabetes, which means foot skin can crack and create entry points for bacteria.
Don’t Miss: How Do You Treat An Ulcer Naturally
What Is A Diabetic Foot Ulcer
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound that occurs in approximately 15 percent of patients with diabetes, and is commonly located on the bottom of the foot. Of those who develop a foot ulcer, six percent will be hospitalized due to infection or other ulcer-related complication.
Diabetes is the leading cause of nontraumatic lower extremity amputations in the United States, and approximately 14 to 24 percent of patients with diabetes who develop a foot ulcer have an amputation. Research, however, has shown that the development of a foot ulcer is preventable.
What Is A Wagner Grade 1 Ulcer
A Grade 1 Ulcer on the Wagner DFU system is considered a superficial ulcer with partial or full-thickness. These wounds may have penetrated the epidermis and dermis, however, they have not reached the tendon or bone yet.
Essentially, this is the farthest stage that a patient would ideally be diagnosed at as the possibility for treatment, and the likelihood of recovery is significantly increased because the wound has not fully penetrated the foot yet.
Read Also: What Can I Eat With Ulcerative Colitis
How Are Foot And Toe Ulcers Treated
The treatment of all ulcers begins with careful skin and foot care. Inspecting your skin is very important, especially for people with diabetes. Detecting and treating foot and toe sores early can help you prevent infection and keep the sore from getting worse.
The goal of treating a foot or toe ulcer is to heal your wound and relieve any pain. Your treatment plan will be individualized based on what medical condition is causing your ulcers. If you cant correct the cause of your ulcer, its likely to come back after treatment.
There are both surgical and nonsurgical treatments for foot and toe ulcers. For early-stage foot and toe ulcers, nonsurgical treatments might work. More advanced ulcers especially ones that are infected might require surgery.
Nonsurgical treatments include:
- Topical wound care.
- Reconstructive surgery using skin grafts.
Prevention Of Ulcer Formation
Meticulous attention to foot care and proper management of minor foot injuries are key to preventing ulcer formation. Daily foot inspection by the patient is the cornerstone of proper foot care. Gentle cleansing with soap and water, followed by the application of topical moisturizers, helps to maintain healthy skin that can better resist breakdown and injury.
The physician should inspect the patient’s shoes for areas of inadequate support or improper fit. While many patients do well with commercially available athletic shoes and thick, absorbent socks, patients with foot deformities or special support needs may benefit from custom shoes. Medicare Part B now covers the purchase of custom shoes when the certifying physician identifies a risk factor for ulcer formation and submits appropriate documentation. A sample documentation form is provided with the monofilament kit used to test patients for peripheral sensory neuropathy.
Minor foot injuries and infections, such as cuts, scrapes, blisters and tinea pedis, can be unintentionally exacerbated by home remedies that impede healing. Patients should be reminded to avoid hot soaks, heating pads and harsh topical agents such as hydrogen peroxide, iodine and astringents . Gentle cleansing of minor wounds and the application of a topical antibiotic to maintain a moist wound environment can help to prevent ulcer formation. In addition, the physician should inspect any minor wound that does not heal rapidly.
Also Check: Ulcerative Colitis Vs Normal Colon
Who Can Get A Diabetic Foot Ulcer
Anyone who has diabetes can develop a foot ulcer. Native Americans, African Americans, Hispanics and older men are more likely to develop ulcers. People who use insulin are at a higher risk of developing a foot ulcer, as are patients with diabetes-related kidney, eye, and heart disease. Being overweight and using alcohol and tobacco also play a role in the development of foot ulcers.
How Do Diabetic Foot Ulcers Form
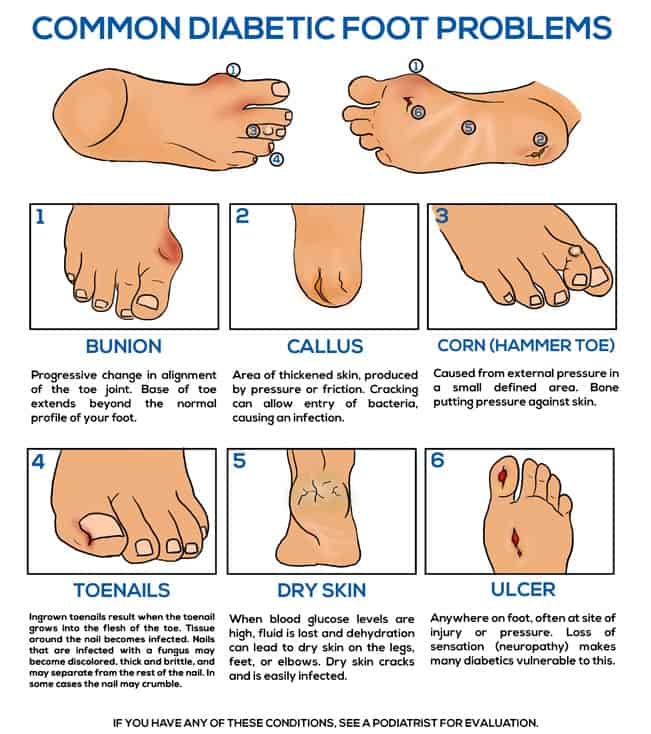
Ulcers form due to a combination of factors, such as lack of feeling in the foot, poor circulation, foot deformities, irritation , and trauma, as well as duration of diabetes. Patients who have diabetes for many years can develop neuropathy, a reduced or complete lack of ability to feel pain in the feet due to nerve damage caused by elevated blood glucose levels over time. The nerve damage often can occur without pain and one may not even be aware of the problem. Your podiatric physician can test feet for neuropathy with a simple and painless tool called a monofilament.
Read Also: Signs And Symptoms Of Diabetic Foot Ulcer
What Are Diabetic Ulcers And What Causes Them
Diabetic ulcers are a serious complication caused by a combination of poor circulation, susceptibility to infection and nerve damage from high blood sugar levels. When there is limited blood flow to the wounded area, the body struggles to heal its skin wounds. So, these wounds develop into diabetic ulcers.
Diabetic ulcers are more prevalent among the diabetic elderly. It is estimated that a quarter of people with diabetes will develop a foot ulcer at some stage. Unfortunately, a quarter of those with ulcers might end up with amputations.
Diabetic Foot Ulcer Symptoms
Normally a wound or sore on the skin would cause pain. But the same loss of feeling in the feet that often contributes to the development of a diabetic foot ulcer means that theres often no pain associated with the ulcer. This can make it difficult for people to realize that an ulcer is even there in the early stages, when treatment is most effective.
Aside from pain, another sign to look for is discharge or drainage from the wound in the socks. Ulcers that have been present for some time and that have become infected may also cause an unpleasant odor.
Recommended Reading: What Is A Skin Ulcer
How Can Diabetic Foot Ulcers Be Prevented
Looking after your feet can help prevent foot ulcers and avoid serious complications. Good foot care includes checking your feet every day, keeping them clean and dry, wearing proper footwear and trying to avoid doing things that could damage them.
Get a foot check at every healthcare visit and seek urgent medical advice if you notice a cut, ulcer or other injury on your foot.
Learn more about diabetes and foot care.
Prediabetes Weight Loss: Can It Help
If you have prediabetes, you are at risk of developing type 2 diabetes because prediabetes means that your blood sugar levels are higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as type 2 diabetes. Fortunately, prediabetes can often be treated with weight loss. In this article, we will explore the relationship between prediabetes and weight loss and find out if losing weight is an effective treatment for prediabetes. We will also cover all other treatment options available to you if you have prediabetes and what causes it.
Recommended Reading: Is Ulcerative Colitis An Infection
How Can I Tell If Im Getting An Ulcer On My Foot Or Toe
When an ulcer is starting to develop on your foot or toe, you might notice changes in your skin like:
As the ulcer gets worse, it can get wider, and longer and deeper sometimes down to the bone. In advanced stages you might see:
- A halo around the center of the wound that feels harder than the skin around it.
- Drainage , which is a sign that you might have an infection.
- A brown discoloration.
Tell Us About The Skin
Our research, for the first time, uncovered a skin-to-brain signaling pathway. It showed that the wound itself could cause subsequent central nervous system and behavioral changes.
We, and others, have observed behavioral and cognitive changes in our patients who have chronic wounds. It is unknown if the wound causes these changes, or they are just associated findings. The idea we proposed is that when a patient gets a wound that heals right away, there is not much sustained signaling of stress to the brain. But a chronic wound keeps activating the sensory receptors for painful stimuli , sending a more continuous skin-to-brain relay. This continuous flare generates brain signals of stress that are translated into behavioral changes.
We carried out research in mice and found that skin wounds result in a relay to the brain. This relay leads to the activation of stress markers, alteration of inflammatory mediators and changes in behavior and cognition. Mice with wounds showed more signs of despair and impaired memory than those with no wounds.
We often see similar behavior in patients with chronic wounds that need daily wound care. Some seem unable to attend to their wounds despite the serious risk of losing their foot to amputation. We also observe depression and cognitive disability reflected in the perception of inability to take care of their wounds. Some even seem to be disassociated from the reality of the serious nature of this problem.
Read Also: Can Tylenol Cause Stomach Ulcers
Complications Of Untreated Diabetic Ulcers
If a diabetic ulcer is not adequately treated, the risk of infection can significantly increase. Abscesses, the spread of disease, gangrene, and eventual amputation are all possible outcomes of poorly treated or neglected diabetic ulcers.
Diabetic foot ulcers can quickly become severe conditions. By treating them as soon as possible, the condition can be remedied before the chance of infection. Serious wounds will not go away on their own and will require prompt attention.
Fortunately, diabetic ulcers can be easily detected. Unlike ulcers that form on the inside of the body, these wounds can be seen and felt. A diabetic ulcer’s symptoms include foot pain, discoloration or numbness, and a deepening wound that will not heal with time. Diabetic ulcers occur in those who have diabetes. The diagnosis of diabetes combined with painful wounds on the bottom of the feet is a good indication that a diabetic ulcer needs treatment.
How Diabetic Foot Ulcers Are Treated
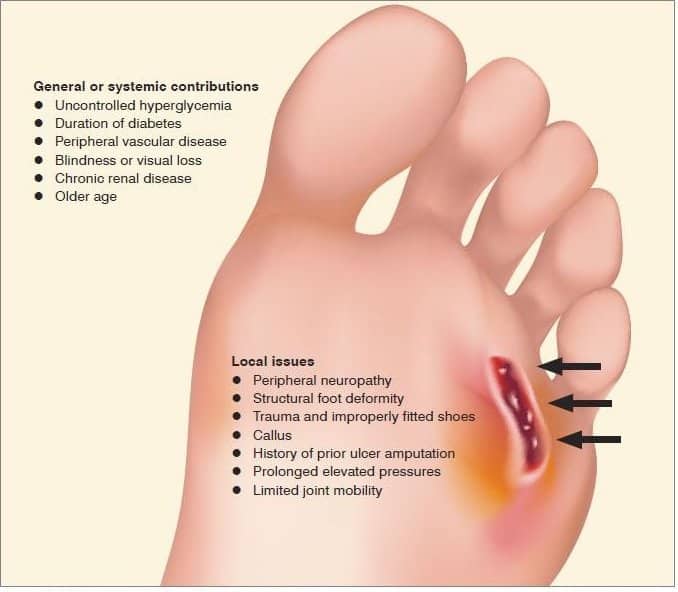
If you do develop a diabetic foot ulcer, your podiatrist will perform debridement of the wound. This means that the doctor will remove the dead skin and tissue from the ulcer to encourage the healing of the tissue. The podiatrist will then apply a dressing to it to prevent an infection. The physician can also perform off-loading to relieve pressure from your foot ulcers, whereby your foot may be placed in a special boot, brace, or cast as your ulcers heal.
Read Also: Foods To Avoid With Peptic Ulcer
What Is A Diabetic Ulcer
A neurogenic ulcer is also known as a diabetic ulcer. Diabetic ulcers are generally found on the bottom of the foot and can occur on either or both feet. Other areas that can be affected include the legs, hands, and even in the folds of skin, around or on the stomach. Diabetic ulcers can be painful. Many people feel embarrassed by their appearance, in addition to the physical pain they experience.
A typical diabetic ulcer on the foot looks like a red sore that manifests in the surface of the skin and can form in a variety of areas. However, sores can occur deeper in the skin. A deep foot ulcer can extend to the tendons and bones of the feet and must be treated quickly. If the condition worsens, the diabetic ulcer will likely become infected.
Heart And Blood Circulation Problems
Cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy is a potentially serious heart and blood circulation problem that’s common in people with diabetic polyneuropathy.
CAN happens when damage to the peripheral nerves disrupts the automatic functions that control your blood circulation and heartbeat.
The 2 main noticeable symptoms of CAN are:
- an inability to exercise for more than a very short period of time
- low blood pressure that can make you feel dizzy or faint when you stand up
Recommended Reading: How Can You Get Rid Of Ulcers