What Makes Yale Medicines Approach To Ulcerative Colitis Stand Out
At our Inflammatory Bowel Disease Program, we know the key to properly managing a patients disease is coordinating care among our specially trained physicians. Our program offers expertise in gastroenterology, surgery, pathology and radiology.
We have a team approach with doctors, physician associates, nurses and surgeons all working together, Dr. Proctor says. Plus, we have more than 25 years of experience to help our patients.
A goal is to empower people with ulcerative colitis to take an active role in their health care and improving their quality of life. To this end, Yale Medicine care providers work hard to educate patients about their disease. In our Inflammatory Bowel Disease Program, a dedicated APRN works closely with patients to offer nutritional resources, medication and surgical options and discuss topics like pregnancy and IBD and depression and chronic disease.
Key Differences Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease
As above discuss, both the diseases are kind of Inflammatory Bowel Disease affecting the colon and gastrointestinal tract and they have few key differences too, which are:
Most Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis Relate To Bowel Movements
The symptoms of ulcerative colitis can vary from person to person, based on where the disease is in the body and how bad the inflammation is.
Most common symptoms:
- Diarrhea , which is often the first symptom.
- Blood in the stool.
- Urgency, or immediate need, to go to the bathroom.
- Increased number of bowel movements.
- Belly pain and cramping.
Ulcerative colitis can cause symptoms throughout your body.
You might have weight loss or other symptoms that affect the entire body. The inflammation of ulcerative colitis can also affect your joints or skin, leading to painful joints and skin rashes. During a flare-up, symptoms may go beyond those that affect the digestive system, including:
- Rashes or patches of red, swollen skin.
- Painful or swollen joints.
- Mouth ulcers.
- Red, irritated eyes.
Keep of track of any symptoms, how often you have them, and how bad they are to talk about with your health care provider.
Also Check: Causes Of Bleeding Ulcers In Stomach
What Can I Expect If I Have A Diagnosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a lifelong condition that can have mild to severe symptoms. For most people, the symptoms come and go. Some people have just one episode and recover. A few others develop a nonstop form that rapidly advances. In up to 30% of people, the disease spreads from the rectum to the colon. When both the rectum and colon are affected, ulcerative symptoms can be worse and happen more often.
You may be able to manage the disease with medications. But surgery to remove your colon and rectum is the only cure. About 30% of people with ulcerative colitis need surgery.
Difference Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease
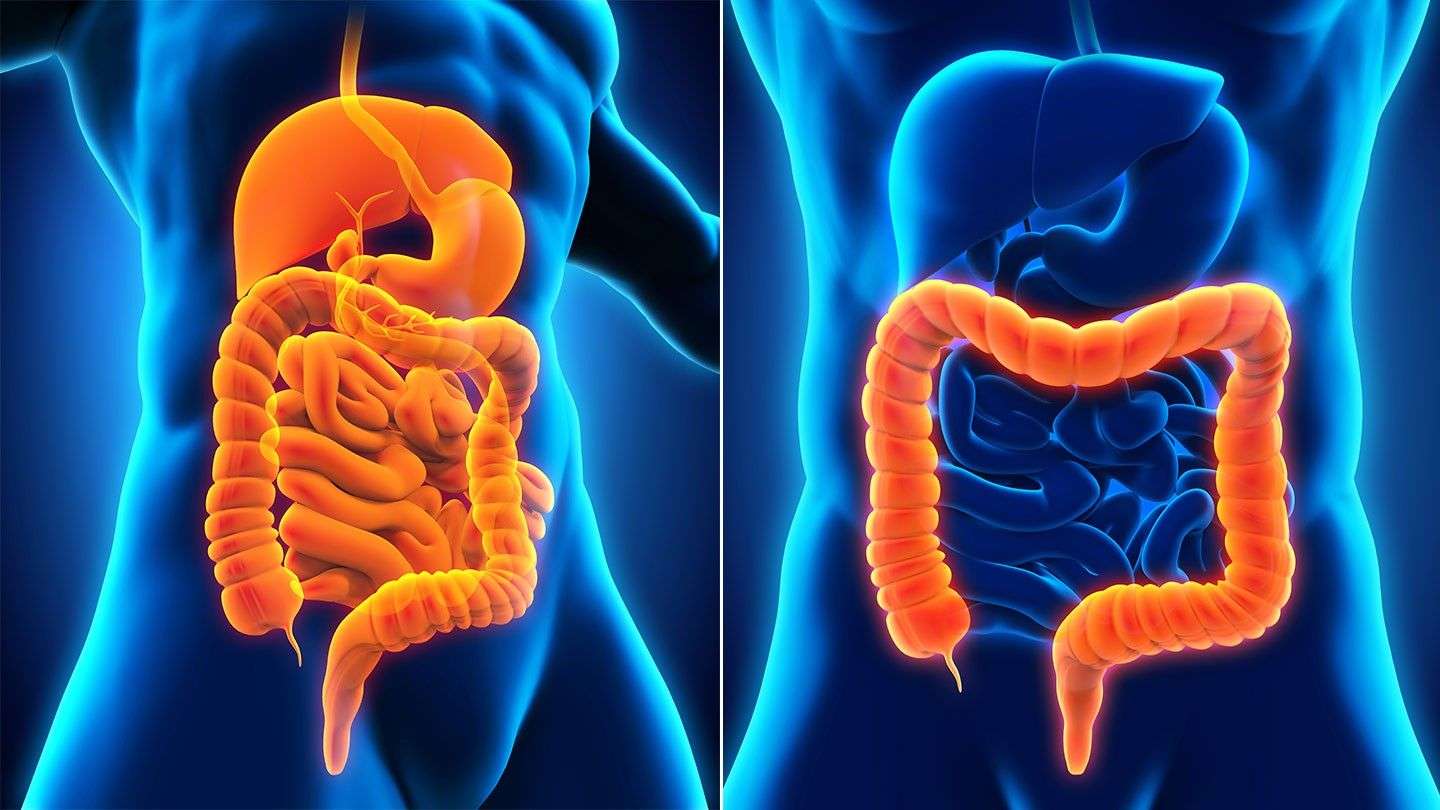
Last updated on by Divanshi G
The key difference between Ulcerative colitis and Crohns disease is that in Ulcerative colitis person usually suffers from abdominal pain, losing weight and superficial inflammation occurs in the innermost linings of the intestinal walls and extended up to colon only in the Crohns disease whole Gastrointestinal tract get inflamed right from the top of mouth to the anus. Inflammatory Bowel Disease can occur at any stage of life.
However, both the disease share almost the same symptoms and can be marked due to the abnormal response of the bodys immune system. The word Inflammatory arose from the Greek word flame which means to be set on fire, it usually starts when bodys immune system takes food, bacteria, and other favorable particles as a foreign body and starts acting against them. These diseases are commonly found in developed countries like the USA, it is believed that due to the lack of germ resistance development in the body has partly contributed to the occurrence of IBD.
People get confused with the Ulcerative colitis and Crohnss disease, hence to know it better it is useful to study the difference between both. Though both the diseases affect the gastrointestinal tract and fall under the umbrella known as Inflammatory Bowel Disease .
Also Check: How Do You Get A Peptic Ulcer
Dietary And Lifestyle Modifications
As most nutrients are absorbed higher up in the digestive tract, those with ulcerative colitis generally do not have nutrient deficiencies however, other factors might influence your nutritional state. Disease symptoms may cause food avoidance, leading to food choices that might not provide a balanced diet. If bleeding is excessive, problems such as anemia may occur, and modifications to the diet will be necessary to compensate for this.
Generally, better overall nutrition provides the body with the means to heal itself, but research and clinical experience show that diet changes alone cannot manage this disease. Depending on the extent and location of inflammation, you may have to follow a special diet, including supplementation. It is important to follow Canadas Food Guide, but this is not always easy for individuals with ulcerative colitis. We encourage you to consult a registered dietitian, who can help set up an effective, personalized nutrition plan by addressing disease-specific deficiencies and your sensitive digestive tract. Some foods may irritate the bowel and increase symptoms even though they do not worsen the disease.
In more severe cases, it might be necessary to allow the bowel time to rest and heal. Specialized diets, easy to digest meal substitutes , and fasting with intravenous feeding can achieve incremental degrees of bowel rest.
Ulcerative Colitis And Colonoscopy
Doctors can use a colonoscopy to diagnose UC or determine the severity of the condition.
Before the procedure, a doctor will likely instruct you to reduce solid foods and switch to a liquid-only diet. Then youll fast for a period of time before the procedure.
Typical colonoscopy prep involves taking a laxative the evening before the procedure, too. This helps eliminate any waste still in the colon and rectum. Doctors can examine a clean colon more easily.
During the procedure, youll lie on your side. Your doctor will give you a sedative to help you relax and prevent any discomfort.
Once the medication takes effect, the doctor will insert a colonoscope into your anus. This device is long and flexible so it can move easily through your GI tract. The colonoscope also has a camera attached so your doctor can see inside the colon.
During the exam, the doctor will look for signs of inflammation and check for precancerous growth called polyps. The doctor may also perform a biopsy. The tissue can be sent to a laboratory for further examination.
If youve been diagnosed with UC, a doctor may conduct periodic colonoscopies to monitor inflammation, damage to your intestines, and healing progress.
These symptoms are sometimes associated with UC complications.
If you havent been diagnosed with UC, see a doctor if you experience multiple symptoms of the condition. They can help determine whether you may have UC or another bowel disease.
Read Also: Is Alcohol Bad For Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative Colitis And Heartburn
Ulcerative colitis comes with a wide range of symptoms, and sometimes, you may wonder if its behind a particular symptom, such as heartburn.
Heartburn refers to a burning sensation in the chest and upper abdomen. Its a relatively common complaint around 15 to 30% of US citizens suffer from it and youre more likely to experience heartburn as you age.
So can ulcerative colitis cause heartburn? Lets find out.
Ulcerative Colitis Is A Type Of Ibd
There are two main types ofinflammatory bowel diseases ulcerative colitis andCrohns disease. Ulcerative colitis is more common worldwide than Crohns disease.
It causes inflammation and sores in the large intestine and may affect part or all of the large intestine.
Ulcerative colitis can happen at any age, but it is more likely to develop in people between the ages of 15 and 30, or older than 60 years of age.
Ulcerative colitis needs to be diagnosed by a health care provider. While there are no cures, there are treatments.
Also Check: Can Ulcerative Colitis Go Into Remission
What Is The Prognosis For People Who Have Inflammatory Bowel Disease
IBD is a lifelong condition, but it shouldnt shorten your life expectancy. With proper treatment, you can prevent flares and have long periods of remission.
Managing a lifelong condition like IBD can be challenging. Its not unusual for people with IBD to become anxious or depressed. Seeing a mental health counselor can help.
Is Heartburn A Sign Of Crohns Disease
Yes, one possible cause of heartburn is Crohns disease, which is closely related to ulcerative colitis.
Crohns disease can affect any part of the GI tract from your mouth to the anus. If it affects your esophagus, you may experience heartburn.
If your heartburn is associated with the following symptoms, you may have Crohns disease:
- Long-term, non-bloody diarrhea
- Abdominal pain, particularly in the right lower area of your belly
- Fat malabsorption if your diarrhea is greasy, smelly, and difficult to flush, you have fat malabsorption
- Fistulae and abscesses in your anal area these are often the first signs of the disease
- Skin rashes, eye inflammation, and painful joints
Because the symptoms of Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis are similar, youll need to work with a gastroenterologist to figure out your condition.
You May Like: Pepto Bismol And Ulcerative Colitis
Who Is At Risk Of Ulcerative Colitis
- Age: Ulcerative colitis may affect any age group, although there are peaks at ages 15 to 30 years, and again at ages 50 to 70 years.
- Race/ethnic background: Ulcerative colitis is more common among caucasians and in people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent.
- Family history: People with a first-degree relative with ulcerative colitis are at greater risk of developing the condition.
What Questions Should I Ask My Healthcare Provider
You may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- What type of IBD do I have?
- Whats the best treatment for me?
- What foods or drinks should I avoid?
- What lifestyle changes should I make?
- Am I at risk for other problems?
- Should I look out for signs of complications?
A note from Cleveland Clinic
Most people with inflammatory bowel disease enjoy active lives. Still, symptoms of Crohns disease and ulcerative colitis can be life-disrupting. Some people go into remission after taking medications. Some people need surgery to deal with severe symptom flare-ups. Your healthcare provider can suggest dietary and lifestyle changes to manage IBD.
Last reviewed by a Cleveland Clinic medical professional on 05/03/2021.
References
You May Like: Do Stomach Ulcers Cause Nausea
Types Of Ulcerative Colitis
The type of ulcerative colitis you have depends on where it is in your body:
- Ulcerative proctitis is usually the mildest form. Itâs only in the rectum, the part of your colon closest to your anus. Rectal bleeding may be the only sign of the disease.
- Proctosigmoiditis happens in your rectum and the lower end of your colon . Youâll have bloody diarrhea, belly cramps, and pain. Youâll have the urge to poop, but you wonât be able to.
- Left-sided colitis causes cramps on that side of your belly. Youâll also have bloody diarrhea, and you might lose weight without trying. Youâll have inflammation from your rectum up through the left side of your colon.
- Pancolitis often affects your entire colon. It can cause severe bouts of bloody diarrhea, belly cramps, pain, fatigue, and major weight loss.
- Acute severe ulcerative colitis is rare. It affects your entire colon and causes severe pain, heavy diarrhea, bleeding, and fever.
How Do I Spot The Signs And Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
The most common symptoms of ulcerative colitis are abdominal pain and diarrhea, which often contains blood or pus.
Symptoms of the disease typically develop gradually and come and go.
Periods without active disease known as remission may last for months or even years.
Over time, ulcerative colitis can progress to cover more of the colon. This typically leads to more severe disease and greater symptoms.
If left untreated, UC can also lead to a number of complications, including:
- Malnutrition
Read Also: Stomach Ulcer Treatment In Homeopathy
Definition Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a severe kind of inflammatory bowel disease , which results in the inflammation of the linings of the large intestine , rectum. It is the kind of chronic conditions, which gradually develops sores on the lining of the colon, it sometimes may affect the entire colon. These ulcers cause bleeding and discharge of pus and mucus.
The patient suffers from bloody diarrhea, loss of appetite, abdominal pain, in worst cases it results in anemia also, due to blood loss. This disease is related to ex-smokers, or nonsmokers. If left untreated it may lead to colon cancer, blood clots, liver disease, osteoporosis, sepsis, dehydration. Also, other post effects are joint pain, joint swelling, skin problems, mouth sores, eye inflammation.
If proper care is not taken, it may lead to colon cancer, so regular screening helps in lowering the risk of colon cancer.
Types of Ulcerative colitis:
- Fulminant Ulcerative colitis.
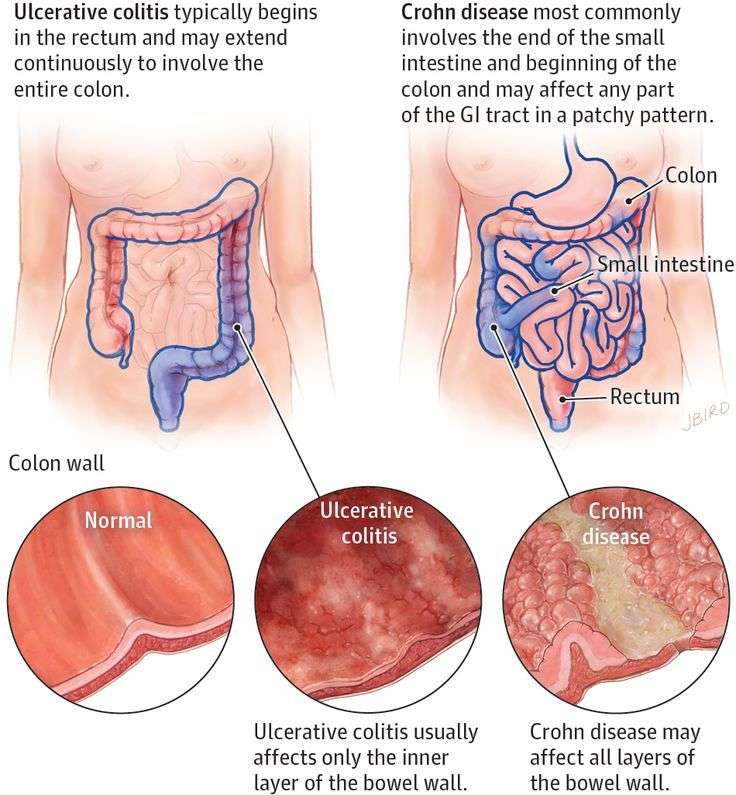
Differences Between Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease
May 14, 2021
There are different but similar symptoms between Ulcerative Colitis and Crohns Disease, both are a kind of inflammatory bowel disease. They both include inflammation in your digestive system. Its important to know which symptoms frequent which disease as Crohns can be more complex to treat. The difference lies mainly in the location of the distress in the gastrointestinal tract and how each of these reacts to the treatment.
Read Also: What Is A Gastric Ulcer And What Is Its Cause
How Is Heartburn Diagnosed
Heartburn is diagnosed by careful history-taking and investigations.
If you present with the classical signs of heartburn, your doctor might start you on a class of drugs called proton pump inhibitors . If your heartburn goes away when you take PPIs, a diagnosis of GERD is confirmed.
However, if you show alarm symptoms, like anemia, persistent vomiting, early satiety, difficulty in swallowing, or weight loss, your doctor might perform an endoscopy to rule out a serious underlying disease like cancer.
Sometimes, esophageal pH monitoring is used to confirm the diagnosis, where the doctor measures the esophageal pH over 24-48 hours via a catheter or capsule.
For what you can do about your heartburn, read the next section.
Ulcerative Colitis And Covid
The coronavirus pandemic has forced everyone to take extra precautions when it comes to health and safety. This is especially true for individuals with a compromised immune system. Although research shows that people living with UC are no more susceptible to catching the virus than the general population, organizations including the American College of Gastroenterology and the Crohns and Colitis Foundation have issued a number of new guidelines to help limit the spread of the infection. Its also recommended that people with ulcerative colitis get the COVID-19 vaccine.
There are also a number of resources available to help people with UC manage these difficult times from medication assistance to virtual therapy for mental health.
Additional reporting by Jordan M. Davidson.
Read Also: Oral Antibiotics For Leg Ulcers
How Ulcerative Colitis Is Treated
Treatment for ulcerative colitis aims to relieve symptoms during a flare-up and prevent symptoms from returning .
In most people, this is achieved by taking medicine, such as:
- aminosalicylates
- corticosteroids
- immunosuppressants
Mild to moderate flare-ups can usually be treated at home. But more severe flare-ups need to be treated in hospital.
If medicines are not effective at controlling your symptoms or your quality of life is significantly affected by your condition, surgery to remove your colon may be an option.
During surgery, your small intestine will either be diverted out of an opening in your abdomen or be used to create an internal pouch that’s connected to your anus called an ileoanal pouch.
More Information About Ulcerative Colitis
The following are some English-language resources that may be useful. Please note that THE MANUAL is not responsible for the content of these resources.
-
Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation of America: General information on Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis, including access to support services
-
United Ostomy Associations of America : Information and support resources for people who live with an ostomy
Don’t Miss: How Serious Is A Stomach Ulcer
Citation Doi And Article Data
Citation:DOI:Assoc Prof Frank GaillardRevisions:see full revision historySystem:
- Lesniowski-Crohn disease versus ulcerative colitis
- Lesniowski-Crohn’s disease versus ulcerative colitis
- Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn’s disease
- Crohn’s disease versus ulcerative colitis
- Crohn disease versus ulcerative colitis
- CD vs UC
- Ulcerative colitis versus Crohn disease
- UC vs CD
Due to the overlap in the clinical presentation of Crohn disease and ulcerative colitis , imaging often has a role to play in distinguishing the two. Distinguishing features include:
- bowel involved
- CD: small bowel 70-80%, only 15-20% have only colonic involvement
- UC: rectal involvement 95%, with terminal ileum only involved in pancolitis