The Rachmilewitz Endoscopic Index
The Rachmilewitz Endoscopic Index uses scores ranging from 03 based on granulation, vascular pattern, mucosal vulnerability, and mucosal damage . If granulation tissue is not present, a score of 0 is given, while its presence results in a score of 2 . Vascular pattern is characterized as normal , faded , or absent , while vulnerability of mucosa is scored as having no bleeding , having contact bleeding , and having spontaneous bleeding . Mucosal damagesuch as erosions and ulcers, mucus, and fibrinis characterized as none , mild or significant . Endoscopic remission is defined as 4 points by this index .
What Role Does Diet And Nutrition Play In Ulcerative Colitis
Diet does not cause the development of ulcerative colitis nor can any special diet cure the disease. However, the foods you or your child eat may play a role in managing symptoms and lengthening the time between flareups.
Some foods may make symptoms worse and should be avoided, especially during flareups. Foods that trigger symptoms are different from person to person. To narrow down what foods affect you, keep track of what you eat each day and how you feel afterward .
Problem foods often include:
- High sugar foods and drinks.
- Carbonated beverages.
- High-fiber foods.
In addition to the problem foods listed above, infants, children and teenagers can also experience issues with:
- Dairy products.
Keep a careful eye on your childs diet and nutrition. Their appetite may decrease during a flareup and they might not eat enough to stay healthy, and grow. Also, the inflammation caused by ulcerative colitis may keep their digestive tract from absorbing enough nutrients. This can also affect your childs health. For these reasons, you may have to increase the amount of calories your child consumes.
Its best to work with your provider and nutritionist to come up with a personalized diet plan if you or your child has ulcerative colitis.
You May Like: Food To Avoid For Ulcer Patient
This Factsheet Is About Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a disease of the rectum and the large bowel, . Ulcerative colitis is thought to affect around 1 in 420. The peak age of incidence between 15-25 years old with a smaller peak occurring between the age of 55 and 65 years old. But it can occur at any age.
INFLAMMATORY BOWEL DISEASE
Ulcerative colitis is one of a group of conditions that are known as Inflammatory bowel diseases, which also includes Crohns disease. Inflammatory bowel disease is different to Irritable Bowel Syndrome , which can cause similar symptoms but does not involve inflammation. The term colitis means the large bowel has become inflamed and if this becomes severe enough ulcers may form in the lining of the large bowel.
Also Check: How Would You Know If You Had A Bleeding Ulcer
The Ulcerative Colitis Colonoscopic Index Of Severity
The Ulcerative Colitis Colonoscopic Index of Severity is another endoscopic scoring system. In a study by Thia et al. , vascular pattern, ulcerations, bleeding-friability, and granularity were all found to have good-to-excellent intra-observer agreement in predicting overall endoscopic severity these components were used to make the UCCIS. Patients with a normal vascular pattern were given a score of 0, while those with a partial loss of pattern were given a 1, and patients with complete obliteration of vascular pattern were given a 2 . Ulcerations were graded as absent , erosions or pinpoint ulcers , multiple shallow ulcers with mucus , deep ulcers , or diffuse ulcers involving more than 30% of the mucosa . In terms of bleeding and friability, mucosa with no bleeding or friability was designated 0, while mucosa with friability and bleeding with minimal touch was rated 1, and tissue with spontaneous bleeding was given 2 . Granularity was divided into 03, with 0 corresponding with no granularity, 1 with fine granularity, and 2 with coarse granularity .
What Is The Pillcam
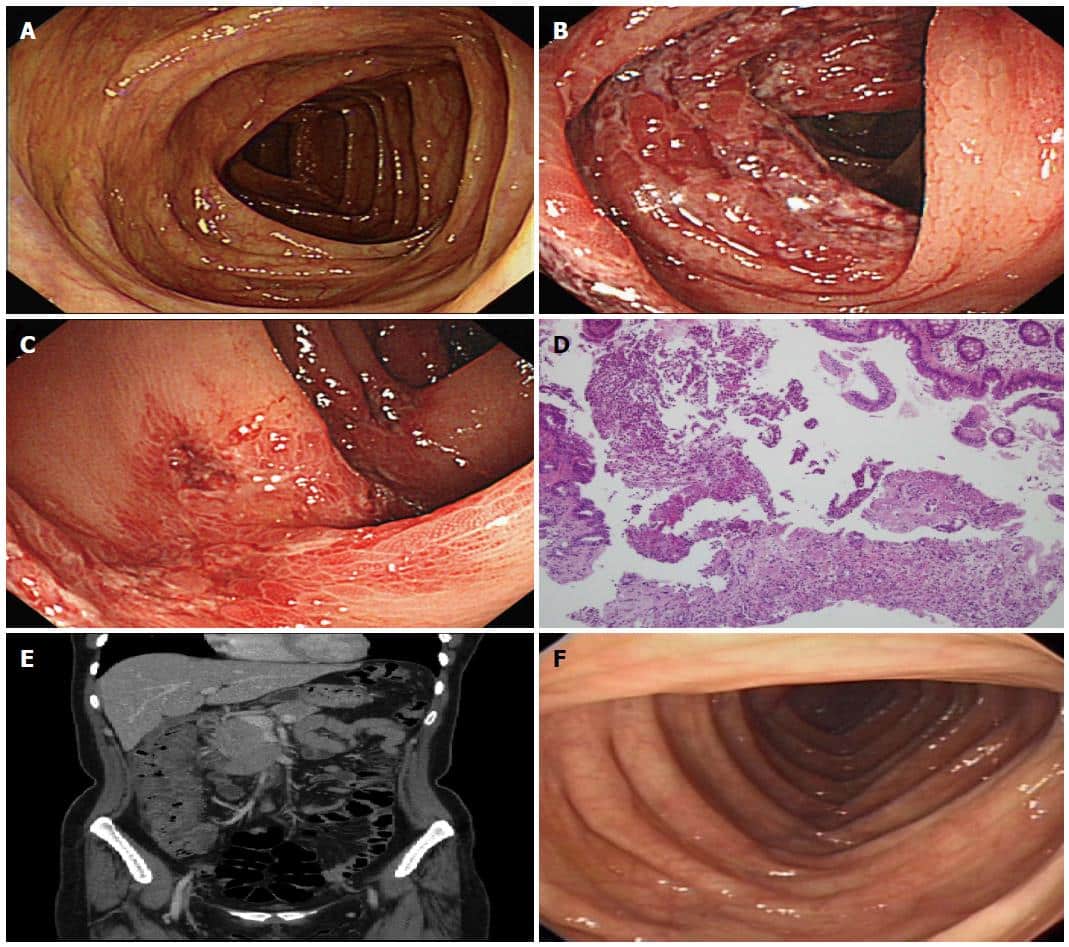
The GI tract is very long and intricate. Because of this, it can be difficult to use an endoscope to see the tract from start to finish. Engineers created a technique called wireless video capsule endoscopy .
It consists of a very small camera the size of a pill that you can swallow. It can capture images of the entire GI tract for the doctor to examine later. This allows your doctor to see areas of your digestive tract that classic endoscopy or imaging cannot show.2
Doctors may also use CT imaging and blood tests. All of these techniques are used together with your symptoms to make a final diagnosis.2
Don’t Miss: Things Not To Eat With A Stomach Ulcer
Symptoms Of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Although Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis target different parts of the digestive tract, they do share some common symptoms, including:
- Stomach pain or cramping
- Low appetite and weight loss
- Diarrhea or bloody stool
- Low-grade fever
In addition to these general symptoms of IBD, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis each have their own negative effects.
If you have Crohn’s disease, you are more likely to experience nausea and vomiting because the condition can affect your stomach. Whereas ulcerative colitis is confined to your bowels. In some cases of Crohn’s, you may also develop mouth sores or have swelling around your eyes.
If you have ulcerative colitis, you are more likely to see blood and pus in your stool and feel pain in your rectum. You may also feel a strong urge to defecate, even if you aren’t able to actually go.
In about 1 in 10 cases of IBD, people experience symptoms of both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Doctors label this overlapping condition “indeterminate colitis.”
Here is a chart showing the different and overlapping symptoms of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis:
The Importance Of Colorectal Cancer Screening
Regular screening for colorectal cancer is important for people living with ulcerative colitis because it increases the likelihood of catching cancer in its earliest, most treatable stages.
Screening is done via a colonoscopy, a procedure in which a long, flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the rectum and used to look at the inside of the colon. This allows your doctor to identify and remove any polyps or other tissue that may be precancerous.
Recent technological advances have improved methods for identifying cancer or precancer in the large intestine during a colonoscopy. For instance, a chromoendoscopy may be used to identify polyps and precancerous changes in the large intestine. This involves using a blue contrast dye to highlight any changes to the lining of the intestine.
According to the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation, those who have had UC symptoms for a period of eight or more years should have a colonoscopy every one to two years. The exception to this is those who have both UC and the liver disease PSC. In this case, surveillance through colonoscopy should begin as soon as a UC diagnosis has been given.
Also Check: Silver Dressing For Leg Ulcers
Mucosal Healing As A Therapeutic Target
Several non-biological medications used in the treatment of UC have been shown to result in mucosal healing mesalazine is one of these. In pooled analysis from the ASCEND I and ASCEND II trials of delayed release oral mesalazine, 80% of patients with moderately active UC, given 4.8 grams/day of mesalazine for six weeks, had documented mucosal healing, compared with 68% of those given 2.4 grams/day of mesalazine for the same time period . In a Cochrane review of 5-ASA use in ulcerative colitis, pooled analysis of four trials showed that patients receiving placebo were more likely to fail to achieve endoscopic remission than patients receiving 5-ASA therapy . In another study, 7 of 21 patients with chronic relapsing UC experienced mucosal healing with sulfasalazine, and nine experienced partial colonoscopic remission with this therapy in the same study, 11 of 21 patients with chronic relapsing UC who received olsalazine had mucosal healing, with nine patients experiencing partial endoscopic remission .
Mucosal healing after effective therapy.
What Are Possible Complications Of Ulcerative Colitis In A Child
In rare cases, this condition can cause death. If your childs condition affects more than just his or her rectum and lower colon, your child has a higher risk for colon cancer. Your child is also at risk for a tear of the bowel wall. This needs to be fixed with surgery. Your child may also have periods of severe bleeding.
Read Also: List Of Foods To Eat When You Have An Ulcer
What Are The Symptoms Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis symptoms often get worse over time. In the beginning, you may notice:
- Diarrhea or urgent bowel movements.
- Abdominal cramping.
- Loss of fluids and nutrients.
Symptoms are similar in pediatric ulcerative colitis and may also include delayed or poor growth. Some ulcerative colitis symptoms in children can mimic other conditions, so it is important to report all symptoms to your pediatrician.
Ulcerative Colitis And Cancer Of The Colon
The chance of developing cancer of the large intestine is higher than average in people who have had ulcerative colitis for several years or more. It is more of a risk if you have frequent flare-ups affecting the whole of the large intestine. For example, about 1 in 10 people who have ulcerative colitis for 20 years which affects much of their large intestine will develop cancer.
Because of this risk, people with ulcerative colitis are usually advised to have their large intestine routinely checked after having had the condition for about 10 years. This involves a look into the large intestine by a flexible telescope every now and then and taking small samples of bowel for examination. It is usually combined with chromoscopy â this is the use of dye spray which shows up suspicious changes more easily. Depending on the findings of this test and on other factors, you will be put into a low, intermediate or high risk category. âOther factorsâ include:
- The amount of intestine affected.
- Whether you have had complications such as polyps. These are small, non-cancerous growths on the inside lining of the colon or rectum.
- Whether you have a family history of cancer.
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence recommends the next colonoscopy/chromoscopy should depend on the degree of risk of developing colon or rectal cancer. After the next test, your risk will be calculated again.
Also Check: Foods You Can Eat With Ulcerative Colitis
Also Check: Va Disability For Ulcerative Colitis
What Can I Expect If I Have A Diagnosis Of Ulcerative Colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a lifelong condition that can have mild to severe symptoms. For most people, the symptoms come and go. Some people have just one episode and recover. A few others develop a nonstop form that rapidly advances. In up to 30% of people, the disease spreads from the rectum to the colon. When both the rectum and colon are affected, ulcerative symptoms can be worse and happen more often.
You may be able to manage the disease with medications. But surgery to remove your colon and rectum is the only cure. About 30% of people with ulcerative colitis need surgery.
Ulcerative Colitis And Crohns Disease
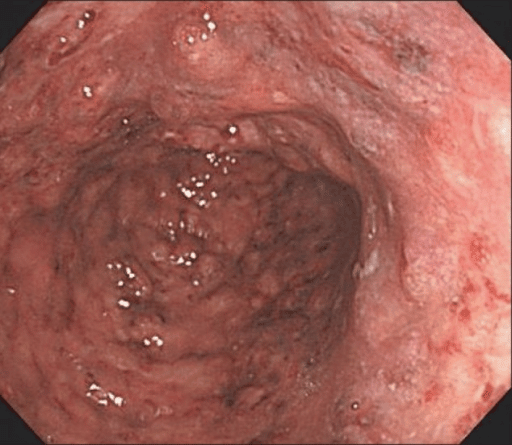
UC mostly presents with rectal inflammation and continuous lesions, while CD presents with discontinuous inflammatory lesions that frequently involve the ileocecal area. Shallow and indiscrete ulcers that involve only the mucosa, with edematous and erythematous changes in the surrounding area may suggest UC . CD can involve not only the colon but also the small bowel, and frequently presents with deep ulcers. The deep ulcers with a longitudinal array create a cobblestone appearance. Sparing of the rectum, presence of perianal disease, and occurrence of strictures and fistulas suggest CD.
Use of serologic markers may help in the differential diagnosis of UC and CD . Anti-Saccharomyces cerevisiae antibodies can be detected in 35% to 50% of CD patients, but in only 1% of patients with UC . On the other hand, perinuclear antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies are detected more frequently in patients with UC. The sensitivity of pANCA+ for UC was reportedly 55.3%, and ASCA+ in combination with pANCA resulted in 54.6% sensitivity for detection of CD . Considering the relatively low sensitivity, serologic test can be the adjunctive tool when differentiation between CD and UC is clinically difficult .
You May Like: Can Ulcerative Colitis Cause Weight Gain
What Should I Ask My Doctor
If you have ulcerative colitis, you may want to ask your healthcare provider:
- How much of my large intestine is affected?
- What risks or side effects can I expect from the medication?
- Should I change my diet?
- Will ulcerative colitis affect my ability to get pregnant?
- What can I do at home to manage my symptoms?
- What are my surgical options?
What Are Canker Sores
Canker sores are small shallow ulcers that occur in the lining of the mouth. The medical term for canker sores is aphthous ulcers. Canker sores start as white to yellowish ulcers that are surrounded by redness. Theyre usually very small but may enlarge to ½ to 1 inch in diameter. Canker sores can be painful and often make eating and talking uncomfortable. There are two types of canker sores:
- Simple canker sores: These may appear three or four times a year and last up to a week. Anyone can get canker sores but they typically occur in people between ages 10 and 20.
- Complex canker sores: These are less common and occur more often in the people who have previously had them.
Read Also: Can You Eat Cheese With Ulcerative Colitis
Recommended Reading: Esophageal Ulcer Symptoms Back Pain
How Do People Prepare For Endoscopy
To prepare for endoscopy, people typically need to adjust their diet for several days beforehand. This reduces the amount of undigested food in their colon.
Patients are asked to follow a low residue diet for 2 to 3 days prior to the procedure, limiting their intake of roughage in the form of fruits, vegetable, and nuts, Dr. Katz told MNT. The day prior to the examination, he continued, patients follow a clear liquid diet.
Doctors also ask people to complete a bowel preparation before endoscopy. This involves taking medication that causes frequent and loose bowel movements.
Patients are instructed to consume one of several available preparations that cause diarrhea so that the colon is cleansed of stool before the examination, said Dr. Katz.
This preparation is usually split, with roughly half consumed the evening prior to the colonoscopy and the other half consumed 3 to 4 hours prior to the procedure, he added.
When it is time for the exam, a nurse will give the patient a sedative so they are semiconscious during the procedure.
pooled the results of past studies on endoscopy to screen for colorectal cancer. They found that the risk of serious side effects was very low.
Major bleeding occurred in 8 in 10,000 colonoscopies and in 2 in 10,000 flexible sigmoidoscopies.
Colon perforation happened in 4 in 10,000 colonoscopies and in 1 in 10,000 flexible sigmoidoscopies. Colon perforation is when something creates a hole in the colon.
What Happens After The Colonoscopy
After the procedure the doctor or nurse may discuss some of the findings with you, or you may be given a follow-up appointment. If biopsies have been taken then the results of these may not be available for several weeks. The results will be sent back to your doctor/consultant who can discuss them with you.
Once the effects of any sedative or anaesthetic have passed you should be able to go home the same day. You should arrange for someone to pick you up from the hospital and to stay with you for 24 hours to ensure all the effects of the medication have passed. During this time you may not be as coordinated as usual and be sleepy. You shouldnt drive, drink alcohol, operate heavy machinery or sign any important documents.
Also Check: How Do You Develop Stomach Ulcers
When You’re In The Hospital
You were in the hospital because you have ulcerative colitis. This is a swelling of the inner lining of your colon and rectum . It damages the lining, causing it to bleed or ooze mucus or pus.
You probably received fluids through an intravenous tube in your vein. You may have received a blood transfusion, nutrition through a feeding tube or IV, and medicines to help stop diarrhea. You may have been given medicines to reduce swelling, prevent or fight infection, or help your immune system.
You may have undergone a colonoscopy. You also may have had surgery. If so, you may have had either an ileostomy or colon resection .
Will Ulcerative Colitis Affect Me Over Time
The effects of ulcerative colitis vary considerably from person to person, based on the nature and severity of their disease. In many cases, the condition does not have much impact on daily life, the ability to work or to enjoy an active social life but does take some getting used to. When it is at an active stage, symptoms such as diarrhoea and abdominal pain often require time away from work, college etc. and can make it difficult to cope going out or even being at home. However, treatment usually makes the symptoms better within days or weeks so normal quality of life can be restored quite quickly. Some severe cases of ulcerative colitis, however, can have a significant impact on peoples lives. This can be due to a weak response to treatment which makes symptom-free remission difficult to achieve and can involve frequent flare ups.
Don’t Miss: Ulcerative Colitis Shortness Of Breath
If Your Endoscopy Doesnt Find Crohns Or Colitis
You might still have Crohns or Colitis even if your endoscopy didnt find anything:
- You might have Microscopic Colitis. This is another form of IBD, which can only be diagnosed after a healthcare professional has taken a look at samples from your bowel under a microscope. You may have to wait a few weeks after your endoscopy to get the results of the biopsy back.
- Your Crohns might be in the small intestine, which can be hard to reach with an endoscope. You may have other tests, like an X-Ray, ultrasound or MRI scan to check for inflammation there. Find out more in our Tests and investigations information.
- You might need to have another endoscopy in case something was missed the first time. This can happen when the bowel preparation did not fully clear out your bowel before the procedure.
If further tests still cant explain your symptoms, you might have another condition. Your healthcare professional will advise you about next steps.
We know it can be frustrating not to have a clear answer to whats making you feel unwell. It can sometimes take a bit of time to reach the correct diagnosis, so you may find it helpful to keep a record of the symptoms you are experiencing so you can show your doctor.