Inpatient Clinical Pathway For Assessment And Managementof Children With Acute Severe/fulminant Ulcerative Colitis
- History and Physical, Initial Diagnostic Testing
- Consultation with GI Fellow
Treatment Day 1
|
|
| Nutrition |
|
| Laboratory Testing | |
| Discuss treatment options with family |
| PUCAI < 35 |
|
|
| PUCAI > 65 |
Posted:Revised:
Evidence
Patient Vs Physician Disease Severity Assessment
Clinical IBD indices completed by adult patients typically do not correspond well with physicians completed indices . Patient-reported outcome measures have increasingly become an important part of disease assessment in adults. Louis et al. employed a three-step approach to develop an IBD descriptive framework. They started with a literature review to identify a broad list of attributes, and subsequently arranged focus group meetings of patients and clinicians to assess the relevance of the attributes. Two rounds of voting were undertaken to name and define each attribute.
A total of 10 attributes were identified: abdominal pain, other disease-related pain, bowel urgency, fatigue, risk of cancer and serious infections within the next 10 years, risk of mild to moderate complications, aesthetic complications related to treatment, emotional status, sexual life, and social life and relationships. They suggested that this descriptive framework should be considered by physicians when discussing IBD treatment options with their patients.
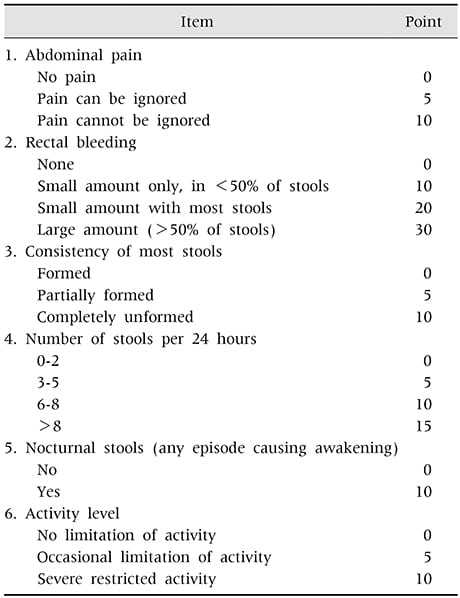
Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis Activity Index
Since colonoscopy is less used in children to assess disease activity, Turner et al. developed a non-invasive activity index for pediatric UC . Item selection was performed judgmentally using a Delphi group of 36 pediatric IBD experts. Item weighting was performed by regression modeling using a prospective cohort of 157 children with UC. Validation was then assessed with a separate prospective cohort of 48 children with UC undergoing full colonoscopy. Responsiveness was also evaluated at a follow-up visit of 75 children using effect size statistics and diagnostic utility approaches. An initial 41 item list was then reduced to 11 by rank order. Two physicians completed the PUCAI on each of the patients in the weighting cohort.
Six clinical items were found to be significant in the regression analysis . The addition of laboratory items or an endoscopic appearance item did not improve the performance of the PUCAI.
In the validation cohort, the PUCAI was highly correlated with the PGA , Mayo score , and colonoscopic appearance . Excellent responsiveness was also found at repeated visits.
In a recent study, Ricciuto et al. showed that children with primary sclerosing cholangitis and IBD in clinical remission, based on PUCAI scores, have a significantly higher risk of active endoscopic and histologic disease than children with UC without PSC. These data indicated that PUCAI scores underperform in the setting of UC with PSC.
Also Check: How Serious Is A Stomach Ulcer
What Does It Mean If Your Childs Pucai Score Is 65 Or Over
About 20%-30% of people with UC will have a PUCAI score of 65 or above at some point in time. If your childâs PUCAI score is 65 or above, they show serious UC symptoms that could mean acute severe ulcerative colitis, a life-threatening UC complication.
Doctors would treat it as a medical emergency requiring quick intervention to avoid further complications like a ruptured bowel, blood infection, or possibly death. They may refer your child to a pediatric gastroenterology unit with surgical support.
A PUCAI score is reliable for monitoring UC symptoms in children. Although you can calculate your childâs PUCAI score when they tell you their symptoms, itâs best to see a doctor for symptom evaluation and treatment progress. Also, contact a doctor if you calculate your childâs PUCAI and they score 65 and above.
Show Sources
Mayo Score / Disease Activity Index For Ulcerative Colitis
- Patients with known ulcerative colitis, particularly when considering changing, adding, or stopping a UC medication this is not a tool to diagnose ulcerative colitis.
- The Mayo Score is the most commonly used scoring system for UC in clinical trials and routine practice .
- The Mayo Score for Ulcerative Colitis was developed to standardize the severity of a patient’s ulcerative colitis symptoms, which is particularly helpful to assess response to treatment over time.
- The Mayo Score for Ulcerative Colitis was originally devised in 1987 for a clinical trial for pH dependent 5-ASA at the Mayo Clinic.
- Comprised of 4 parts: stool frequency, rectal bleeding, endoscopic findings and physicians global assessment, each scored from 0-3.
- The physicians global assessment accounts for other signs/symptoms including abdominal pain, physical exam findings , functional status, and the patients overall sense of well being.
- Total scores range from 0-12 with higher scores indicating increased severity of disease.
- Response to therapy is defined differently in each trial, but most use a decrease of 3 or more points.
- Remission is often defined as a total score of 2 or less with all individual categories 1. Occasionally, remission is defined stringently as a score of 0.
- Most clinical trials define mucosal healing as an endoscopic score of 0 or 1, although numerous other endoscopic scoring systems exist .
Points to keep in mind:
Recommended Reading: Can You Donate Blood If You Have Ulcerative Colitis
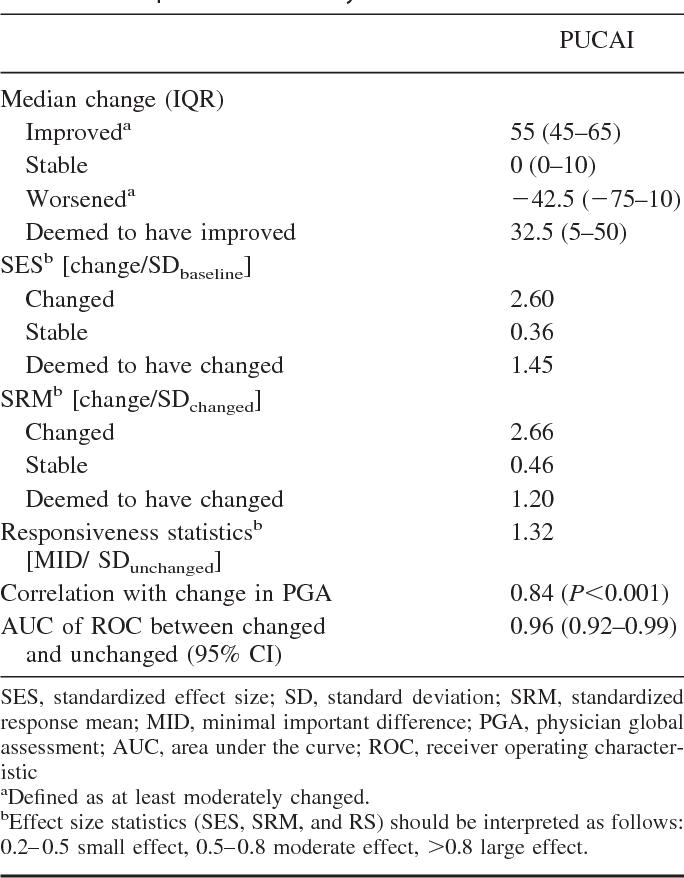
Responsiveness Mdc And The Mid
A total of 213 children had a follow-up visit recorded and thus contributed to the responsiveness analysis. The PUCAI differentiated well the different groups of improvement, unchanged and deterioration, as judged by the change in PGA . The 3 conceptual methods to evaluate responsiveness indicated high responsiveness of the PUCAI across all statistical methods .
Distribution of the PUCAI according to the change in physicians’ global assessment . The minimal important difference was determined by ROC curve, finding the best cutoff on the PUCAI to differentiate change: small change denotes a change of 1 category on the PGA, moderate change denotes a change in 2 categories, and large change, 3 categories.
The MID of small change in PUCAI was 10 points . The MID for moderate improvement was at least 30 points . It was impossible to calculate the MID for moderate worsening since there were only 2 patients in this subgroup.
The reliable change index, reflecting the MDC, was 12.2 points . In agreement, 0.5 standard deviation of PUCAI was 11.9 points. These data imply that the PUCAI unit to be considered real beyond interrater variability is 12 points, similar to the MID found for small change.
Magnetic Resonance Enterography Global Score
This score, developed in 2014, modified the CMI by the inclusion of additional features . The score involves dividing the small and large intestine into nine sections, with summation of scores for each section to provide a total score. MEGS was validated in patients with CD and compared favorably to other markers such as fecal calprotectin.
Recently, MEGS was evaluated in 52 Chinese children with CD and compared directly to SES-CD scores in each child . MEGS scores correlated with endoscopic scores . Further, MEGS scores predicted disease activity with sensitivity of 88% and specificity of 75%.
Don’t Miss: Is Salmon Good For Ulcerative Colitis
Initial Pediatric Severity Scores
The first activity scoring systems for children with CD were developed in the 1970’s. Whittington and colleagues reported the evaluation of disease severity in a series of 16 adolescents. The scoring system included patient symptoms, physical examination findings and the results of two blood markers: erythrocyte sedimentation rate and albumin. Severity was assessed on a six-point scale, where 1 was asymptomatic with normal bloods and 6 was incapacitating symptoms. This scale was used in the description of a small group of patients to delineate response to medical therapies over time. It did not include assessment of growth, was not formally evaluated or validated and has not been reported in any other patient groups.
Two years later, Lloyd-Still and Green reported their scoring system for children with IBD. Included within this score were growth data, endoscopic findings, and radiological findings. Severity correlated with serum albumin levels. While the score was reported to be easy to use and reliable between reporters, it required invasive investigations and has not been used widely.
Pediatric Crohn Disease Activity Index
The Pediatric Crohn Disease Activity Index was developed in 1990 with the input of 30 pediatric gastroenterologists from 12 North American centers with the goal to be a tool that could be used easily and reproducibly for longitudinal assessment of disease activity in multi-center studies . The tool is comprised of 11 items completed by a physician with scores ranging from 0 to 100, with higher scores indicating worse disease activity. The development and validation of the tool included collection of relevant data from 131 children with CD. Physicians completed a modified HBI and provided Physician Global Assessment scores for each of the patients.
The analysis of the data arising from these assessments showed that the PCDAI correlated well with HBI and PGA scores. It also provided delineation between remission and degrees of severity. The key benefits of the PCDAI over the HBI was the inclusion of growth parameters and objective markers of inflammation, whilst providing a clear scoring range.
Otley et al. subsequently compared the feasibility, validity, and responsiveness of the PCDAI compared to the CDAI in the assessment of disease activity in children with CD. This study demonstrated that the PCDAI was superior to the CDAI in discriminating between levels of disease activity.
You May Like: How Do You Diagnose A Stomach Ulcer
Can You Calculate Your Childs Pucai Score
Endoscopy is a test that looks at a personâs digestive tract using a flexible tube with a special camera. However, because of its cost and the invasive nature of endoscopy, itâs not always a good choice for monitoring UC in children.
Researchers created the PUCAI score in 2007 as a substitute for endoscopy. Since then, researchers have used the PUCAI in studies to measure how well people respond to UC medicines. Studies have found that the PUCAI is also useful in hospital settings to help manage UC in children.
Doctors can use the PUCAI to monitor a childâs symptoms and response to treatment. They can also use it to predict and manage complications and emergency cases.
But can you or your child complete the PUCAI? A 2011 study showed PUCAI scores calculated by doctors were similar to those calculated by their patients, especially those with moderate to severe symptoms.
There was less â but still high â agreement between patient-completed and doctor-completed PUCAI scores when the patients had little or no symptoms.
The researchers said that patient-based PUCAI tools could be useful for helping them be more aware of their symptoms and communicate with their doctors. Still, the study showed that scores calculated by doctors and patients do not always agree, so a patient-based PUCAI score canât replace a doctorâs evaluation.
Pediatric Inflammatory Crohn’s Mre Index
The PICMI score was developed and validated in Toronto, Canada . The imaging findings of 48 children with CD were evaluated. The MRE signs correlated with wPCDAI scores, and several findings were more strongly associated with inflammation. This score has not yet been evaluated further or in other settings.
Don’t Miss: Boots To Prevent Pressure Ulcers
Magnetic Resonance Index Of Activity
The MaRIA score is derived from assessment of mural thickness, contrast enhancement, oedema and ulceration using a specific formula . The total score is derived from the summation of scores for each section of the gut.
In a recent study Minordi et al. evaluated the findings from repeated MRE in 46 individuals with CD before and after medical therapy. MaRIA scores reflected clinical responses .
The MaRIA has been evaluated in one recent pediatric study . This sub-study of the ImageKids study included 237 children with CD. Most had completed ileocolonoscopythe remainder did not have ileal intubation. Overall MaRIA scores agreed strongly with the ileal endoscopic scores . The agreement between the colonic segment endoscopic scores and MaRIA scores ranged between 68 and 85%. The authors developed a model to be able to predict the ileal SES-CD scores in the subset of children who did not have ileal intubation.
Study Design And Overview

A Delphi group of pediatric IBD experts was established to aid with item generation, reduction, and gradation. A Delphi technique involves an iterative, multistep process to reach a consensus for a specified question, when the experts are not physically together. The responses of all members of the Delphi group are summarized by an expert panel, processed, and resent to the group for further comments until consensus is reached. Between November 2005 and November 2006, 2 separate prospective
Don’t Miss: Ulcerated Nodular Basal Cell Carcinoma
Cutoffs Of Disease Activity
The PUCAI differentiated very well the different categories of disease activity captured by the PGA . The best cutoff to differentiate remission from active disease was < 10 points , to differentiate mild from moderate disease activity at least 30 points , and moderate disease activity from severe at least 65 points .
Distribution of the PUCAI according to disease activity as measured by physicians’ global assessment . The numbers on the right denote the best cutoff scores to differentiate disease activity, obtained by serial ROC curves.
Appraisal Of The Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis Activity Index
Reprints: Dan Turner, MD, PhD, Pediatric Gastroenterology Unit, Shaare Zedek Medical Center, POB 3235, Jerusalem 91031, Israel .
The registry is maintained with support from Centocor, Inc., AstraZeneca, PLC, and the participating institutions.
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases
You May Like: What Foods Irritate Stomach Ulcers
How To Calculate The Pucai Score
The PUCAI score ranges from 0 to 85 and is defined as:
- Remission : less than 10
- Mild: 10-34
- Predict the course of the disease over time
- Know when to recommend other treatments in severe cases
Experts recommend that doctors check a childâs PUCAI score during every visit and reevaluate treatment if their score is above 10.
What Is A Pucai Score
A PUCAI score is a number that tells how serious your childâs symptoms are. Doctors reach this number by using a scoring system for measuring the extent and severity of UC in children without taking a lab test.
The doctor listens to your childâs or your report of their symptoms and translates them into the PUCAI. The PUCAI takes less than a minute to calculate and can be used to monitor symptoms in both adults and children.
Based on typical symptoms, the PUCAI looks at six items to arrive at a score:
You May Like: Medications Used For Ulcerative Colitis
Crohn’s Disease Endoscopic Index Of Severity
The CDEIS assesses the endoscopic appearance in four colonic segments and the terminal ileum . The surface is assessed in terms of ulceration and stenosis and the extent of these changes, with a score ranging from 0 to the maximum score of 44. This scoring system has been utilized in clinical trial settings, but there is more discrepancy about the optimal cut-off to indicate endoscopic response and remission.
Magnetic Resonance Enterography Severity Scores
Magnetic resonance enterography is now well-established as a cross-sectional imaging modality to ascertain the presence or extent of small bowel disease in individuals with CD and to delineate disease-related complications such as small bowel stricture. MRE has significant benefits over other cross-sectional imaging methods, such as computed tomography, due to avoidance of ionizing radiation, especially in children and adolescents. Several tools have been developed to provide objective assessment of MRE findings, with most assessments focusing on adult patients rather than children.
You May Like: Icd 10 Venous Stasis Ulcer
Item Generation Reduction And Grading
Of the 48 pediatric IBD experts contacted, 36 responded and served as the Delphi group. A list of 21 potential items was generated by the expert panel, and the Delphi group added another 20. Eleven variables, which were ranked significantly higher than the others, were graded by the Delphi group from 1, important, to 11, least important . One item, rectal urgency, was removed because of perceived difficulties in applying this variable to young children. C-reactive protein ,
An Overview Of Tools To Score Severity In Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- 1Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition Institute, Ruth Children’s Hospital of Haifa, Rambam Medical Center, Faculty of Medicine, Technion, Haifa, Israel
- 2Department of Paediatrics, University of Otago Christchurch, Christchurch, New Zealand
Background and Aims: The management of IBD entails the use of various treatments in order to induce and maintain remission. The assessment of IBD disease activity is based on a combination of symptoms, clinical findings, imaging, and endoscopic procedures. As in any disease, reliable assessment of disease activity or severity is required in order to plan relevant follow-up, decide on appropriate investigations, determine the best treatment option and subsequently assess response to treatment. It is important for proper documentation, follow-up, assessment of response to treatment and communication, especially in patients with IBD, to talk the same language by using validated and widely used scores for disease activity, endoscopic and radiologic activity, and patient reported outcomes both for clinical practice and research. This review aims to highlight key tools available for the assessment of disease activity or severity in individuals with IBD.
Although some available scoring tools are appropriate for children with IBD, others require consideration. The development and use of pediatric-specific tools is relevant and appropriate to optimal care of children and adolescents with IBD.
Also Check: Could I Have A Stomach Ulcer